Averaging the results from two independent participants improved screening accuracy, whether participants were looking at baggage scans or mammograms, according to findings published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
The research findings, reported by researchers at Brunel University, suggest that having multiple screeners could improve the detection of rare items in real-world contexts, such as airport security, radiology and military reconnaissance.
"There is a known problem with detecting rare targets," said study author Jennifer E Corbett, an honorary lecturer for Brunel's College of Health and Life Sciences. "When you go to the airport, they always seem to find the bottle of water in your bag – it's a very common item, so people have a mental template. They'll just find it. But with rare targets like weapons and guns, people see these far less frequently, so are more likely to miss them."

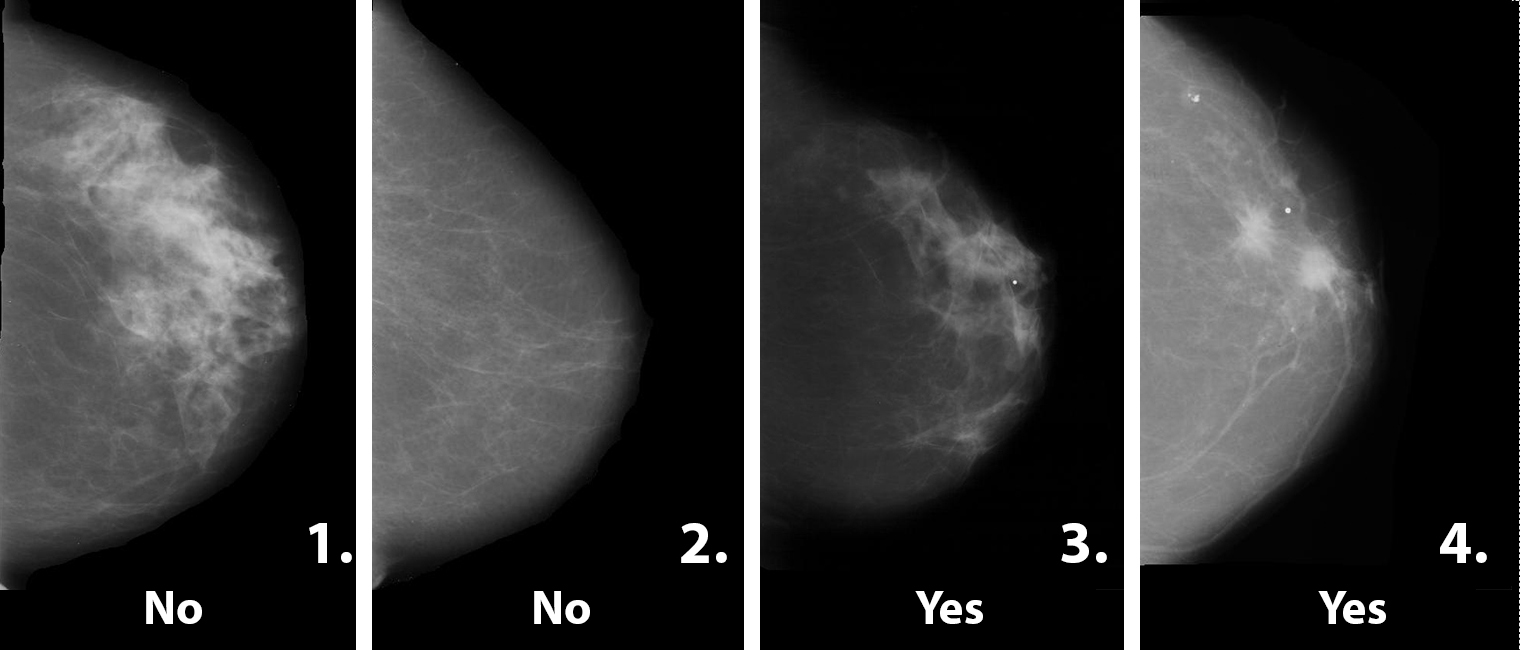
Can you tell which of these mammograms shows a tumor? Check your answers below. Source: Brunel University
Corbett, who coauthored the paper with Brunel researcher Jaap Munneke, says the problem lies with the human visual system, which is only capable of processing a few objects in detail at any given moment. The brain averages out redundant and specific information, filling in the spaces based on prior knowledge. As a result, infrequent objects – those that the observers aren't expecting to see – are often missed.
However, two people independently looking at the same scan perceive it differently, significantly increasing the possibility of infrequent items being spotted.
"We found that when we pair the estimates of two people who don't know they're working together – they have no interaction whatsoever – there is a huge improvement in detection, just by capitalizing on the diversity of people's judgments," said Corbett.
To test their ideas, Corbett and Munneke conducted two experiments – one which challenged participants to undertake airport screening and the other mammogram screening.
In the airport screening experiment, 16 participants, who had no experience with security screening, saw an image containing nine objects for half a second. They then indicated whether they'd like to call the image back, based on whether they detected a target object.
"The experiment tested weapons detection as well as simple detection tasks," said Corbett. "We found that not only did pairing observers estimates improve detection in both types of tasks, but that pairing individuals' estimates from the simple task in a way that maximized the decorrelated patterns actually improved the performance in the separate weapons task."
The researchers discovered that when they paired the detections of two people who worked individually and independently, they not only saw an increase in the detection of rare objects, but also a reduction in the likelihood of harmless items being wrongly flagged as suspicious.
For the second experiment, 18 participants learned how to identify a tumor on a mammogram. They then saw 400 unique scans, 5% of which had a tumor present, and then another 400, of which 50% had a tumor present.
In both cases, a significant increase in detection rate was observed when two individuals' results were averaged.
"The task is not so different between airport scanner and a radiologist – the idea is you're looking for something you have knowledge of but see infrequently," said Corbett. "It doesn't matter though whether it's a tumor or a weapon or something else, averaging two different perceptions of the same scene increases detection."
The researchers say their detection method is a marked improvement over those currently used in airport and radiological screening, as it significantly reduces the time someone needs to look at a scan.
"The method we propose is probably the best candidate for maximizing the resources of a limited pool of highly trained experts needing to detect rare targets in a lot of images," said Corbett. "Obviously the limit here is that it requires a second set of eyes, but we're now looking for ways to use a deep-learning algorithm to cover the aspects of the images which are causing these decorrelations. We can then pair a single person with the algorithm."
All data have been made publicly available via the Open Science Framework. The complete Open Practices Disclosure for this article is available online. This article has received the badge for Open Data.
Correct answers. Source: Brunel University
https://ift.tt/2Qd9qYj
 Objective: The aim of this study is to examine the relationship between the sex pay gap in a large academic department of surgery and a recently instituted structured compensation plan. Summary of Background Data: A recent large study found that after controlling for measures of academic and clinical productivity, male physicians earned nearly $20,000 more annually than female physicians. Increased salary transparency has been proposed as a method to reduce this disparity. Methods: A new structured compensation plan was developed to improve transparency of compensation and financial viability of each division. The total compensations of each faculty member before and after the new compensation plan were calculated. Salaries were compared with the Association of Academic Medical Colleges (AAMC) median value based on specialty, region, academic rank, stratified by sex and compared. Work relative value units (wRVUs) were calculated for each faculty member during the entire study period, stratified by sex and compared. Results: Among 44 eligible surgeons (33 men and 11 women), a sex pay gap existed with male surgeon salaries significantly higher than female surgeon salaries [56% (8 to 213) vs 26% (1 to 64); P
Objective: The aim of this study is to examine the relationship between the sex pay gap in a large academic department of surgery and a recently instituted structured compensation plan. Summary of Background Data: A recent large study found that after controlling for measures of academic and clinical productivity, male physicians earned nearly $20,000 more annually than female physicians. Increased salary transparency has been proposed as a method to reduce this disparity. Methods: A new structured compensation plan was developed to improve transparency of compensation and financial viability of each division. The total compensations of each faculty member before and after the new compensation plan were calculated. Salaries were compared with the Association of Academic Medical Colleges (AAMC) median value based on specialty, region, academic rank, stratified by sex and compared. Work relative value units (wRVUs) were calculated for each faculty member during the entire study period, stratified by sex and compared. Results: Among 44 eligible surgeons (33 men and 11 women), a sex pay gap existed with male surgeon salaries significantly higher than female surgeon salaries [56% (8 to 213) vs 26% (1 to 64); P





