|
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(138)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (74)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (64)
-
►
2022
(849)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (61)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (74)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (65)
-
►
2021
(2936)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (59)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (180)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (325)
-
▼
2020
(1624)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (293)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(376)
-
▼
Νοε 15
(17)
- Assessment of a patient-reported outcome measure i...
- Vascular and metabolic risk factor differences pri...
- Efficacy and safety of early treatment with sarilu...
- Association of nephrolithiasis with the risk of ca...
- ASPIRE trial: study protocol for a double-blind ra...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3377: Tumor Microenvironme...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3378: The Non-Coding Lands...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3379: Osteopontin: A Key R...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3381: Outcome of Targeted ...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3380: Cancer-Associated An...
- Clinical Challenges in the Management of Hormone R...
- Ethosuximide Induced Macroglossia and Oropharyngea...
- JPM, Vol. 10, Pages 231: Ocular Vascular Changes i...
- Contralateral tension pneumothorax during video-as...
- A Subset of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas Expre...
- Human papilloma virus (HPV) integration signature ...
- Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3382: Comprehensive Gene M...
-
▼
Νοε 15
(17)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (234)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(13362)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (5586)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5696)
-
►
2018
(66471)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (5242)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (5478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (4835)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5592)
-
►
2017
(44259)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (5110)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (5105)
-
►
2016
(7467)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (514)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (1038)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (793)
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
Κυριακή 15 Νοεμβρίου 2020
Assessment of a patient-reported outcome measure in men with prostate cancer who had radical surgery: a Rasch analysis
Vascular and metabolic risk factor differences prior to dementia diagnosis: a multidatabase case-control study using European electronic health records
|
Efficacy and safety of early treatment with sarilumab in hospitalised adults with COVID-19 presenting cytokine release syndrome (SARICOR STUDY): protocol of a phase II, open-label, randomised, multicentre, controlled clinical trial
|
Association of nephrolithiasis with the risk of cardiovascular diseases: a longitudinal follow-up study using a national health screening cohort
|
ASPIRE trial: study protocol for a double-blind randomised controlled trial of aspirin for overheating during exercise in multiple sclerosis
|
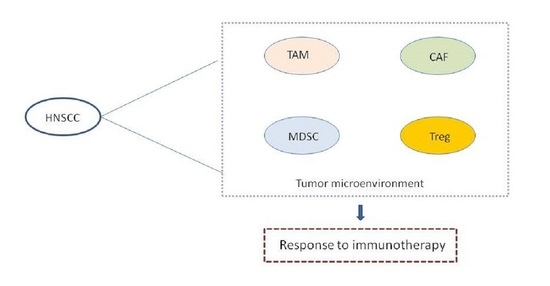
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3377: Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy Response in Head and Neck Cancer
|
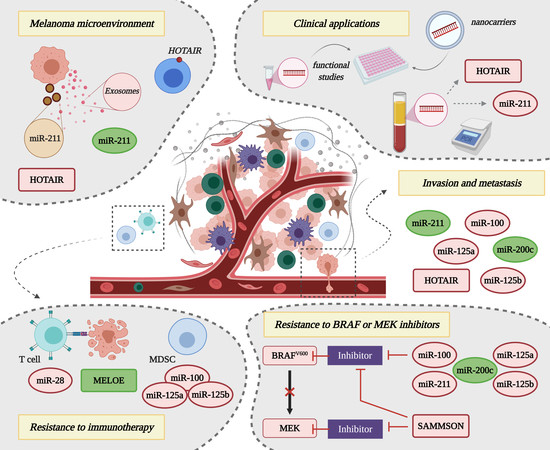
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3378: The Non-Coding Landscape of Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma: A Possible Route to Efficient Targeted Therapy
|
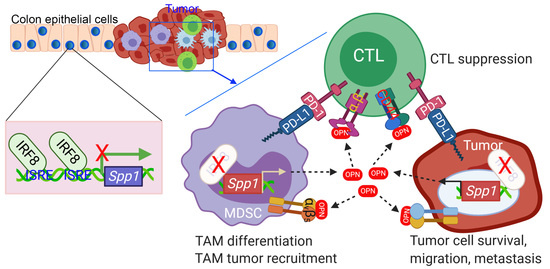
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3379: Osteopontin: A Key Regulator of Tumor Progression and Immunomodulation
|
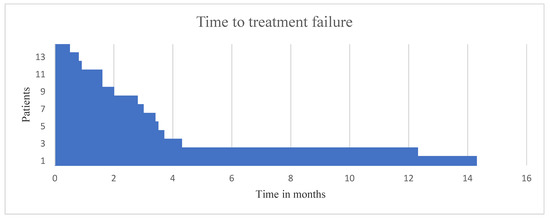
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3381: Outcome of Targeted Therapy Recommendations for Metastatic and Recurrent Head and Neck Cancers
|
Cancers, Vol. 12, Pages 3380: Cancer-Associated Angiogenesis: The Endothelial Cell as a Checkpoint for Immunological Patrolling
|
Clinical Challenges in the Management of Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Literature Review
|
-
This protocol presents an in vitro live-imaging phagocytosis assay to measure the phagocytic capacity of astrocytes. Purified rat astrocyt...
-
Association française pour l'étude du cancer [Imatinib in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in Morocco]. Related Articles [Im...
-
A Case of Miller Fisher Syndrome Due to the Use of Cemiplimab : No abstract available Miller Fisher syndrome is a rare, acquired n...