Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(138)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (74)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (64)
-
►
2022
(849)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (61)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (74)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (65)
-
►
2021
(2936)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (59)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (180)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (325)
-
►
2020
(1624)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (293)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (234)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(13362)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (5586)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5696)
-
▼
2018
(66471)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (5242)
-
▼
Νοεμβρίου
(5789)
-
▼
Νοε 16
(228)
- On Loneliness: Where Politics, Medicine, Psycholog...
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Role on Notal...
- Onabotulinum Toxin A Injections Into the Salivary ...
- Co-morbidities Associated With Early Mortality in ...
- Improvement During Inpatient Rehabilitation Among ...
- The Effect of Stabilization Exercises on Pain, Dis...
- Ultrasonographic Findings in a Latissimus Dorsi In...
- State of the States: Growing PhysiatryAssociation ...
- Association of Admission Functional Status and Ass...
- Efficacy of Compression Gloves in the Rehabilitati...
- Letter to the Editor About the Article "Aquatic Ex...
- Bone Marrow Fat Physiology in Relation to Skeletal...
- Reversible Visual Field Defect After Isolated Intr...
- Evidence-Based Physiatry: Pediatric Neuromuscular ...
- Respiratory Synkinesis Seen in the Biceps Brachii ...
- MGMT Testing in Glioblastomas: Pitfalls and Opport...
- Use of polygenic risk scores of nicotine metabolis...
- A review discussing the use of polyethylene glycol...
- Evaluation of 0.2% delmopinol mouth rinse for prev...
- SEOM clinical guidelines for the treatment of non-...
- Understanding Moment‐to‐Moment Processing of Visua...
- Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy: Risk Factors,...
- Endoscopic ultrasound‐guided choledochoduodenostom...
- Endoscopic radiofrequency biliary ablation treatme...
- Use it or lose it? Effects of age, experience, and...
- Cortisol secretion moderates the association betwe...
- NMT1 inhibition modulates breast cancer progressio...
- The influence of the nylon balloon stiffness on th...
- Suicide with an unusual home-manufactured firearm
- Cancer immunotherapy of patients with HIV infection
- Bridging the gap between vaccination with Bacille ...
- Two MYC Homology Boxes Drive Tumorigenesis [Resear...
- A Developed STING Agonist Has Systemic Antitumor A...
- Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma in an adult with Prote...
- Exercise testing and adipokine levels for the eval...
- Thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in invas...
- Caregiver’s perception of epilepsy treatment, qual...
- Understanding neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalop...
- Matrix metalloproteinases in ureteropelvic junctio...
- Isolated sphenochoanal polyp: report of three cases
- Endovascular treatment of an axillary artery pseud...
- Syncope in a patient with tortuous right common ca...
- Soft Tissue Disorders of the Mouth
- Forthcoming Issues
- Tracheostomy Emergencies
- Contents
- Contributors
- Dental Emergencies
- Peripheral Vertigo
- Ear, Nose, and Throat Emergencies
- CME Accreditation Page
- Ears, Nose, and Throat Emergencies
- Foreign Bodies of the Ear, Nose and Throat
- Ear, Nose, and Throat Emergencies
- Sinusitis Update
- Erratum
- Epistaxis
- The Diagnosis and Management of Facial Bone Fractures
- Heteroatom‐Doped Carbon Materials for Hydrazine Ox...
- Organic Photovoltaics with Multiple Donor–Acceptor...
- Enzyme‐Instructed Supramolecular Self‐Assembly wit...
- Rollable, Stretchable, and Reconfigurable Graphene...
- Design for Highly Piezoelectric and Visible/Near‐I...
- Direct CVD Growth of Graphene on Traditional Glass...
- The Absence and Importance of Operando Techniques ...
- {-}{-}{-}{-}Immunotherapy for Glioblastoma: Adopti...
- Inhibition of LEF1-mediated DCLK1 by Niclosamide A...
- Neutrophil extracellular traps induced by IL-8 pro...
- Predicting Treatment Response Based on RNA Express...
- Only Human
- Man With Abdominal Pain and Bilious Emesis
- Man With Left-Sided Neck Pain
- Editors
- In reply:
- Elderly Woman With Abnormal ECG
- Elderly Woman With Abdominal Pain
- Elderly Female With Syncope
- What's Coming in Annals ● January 2019
- Table of Contents
- New Emergency Nurse Practitioner Certification Rol...
- Outpatient Pulmonary Embolism Management: If You W...
- Research in Emergency Medicine: Building the Inves...
- Annals Q&A With Dr. Stephen Bergman
- Global Research Highlights
- Calendar
- Classified
- Information for Readers
- Woman With Foreign Body on Her Tongue
- Woman With Neck Pain
- Reply
- Use of Blood Biomarkers in the Assessment of Sport...
- Effects of Intravenous Cold Saline on Hyperthermic...
- Risks of Exertional Rhabdomyolysis With Blood Flow...
- Effects of 12-Week Resistance Exercise on Electroe...
- Reactive Osteochondromatous Lesion of the Femoral ...
- Postexercise Hypotension as a Predictor for Long-T...
- Reply
- TRest as a New Diagnostic Variable for Chronic Exe...
- Strengths, Limitations, and Geographical Discrepan...
- Shoulder Injuries in Canoeing and Kayaking
-
▼
Νοε 16
(228)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (5478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (4835)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5592)
-
►
2017
(44259)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (5110)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (5105)
-
►
2016
(7467)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (514)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (1038)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (793)
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
Παρασκευή 16 Νοεμβρίου 2018
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Role on Notalgia Paresthetica: Case Report and Treatment Review
 Notalgia paresthetica is a rarely reported T2–T6 sensory neuropathy whose etiology and treatment are not fully established. Although it is believed to be common in dermatological practice, it remains underrecognized, underdiagnosed, and therefore underreported. This case-report provides a physical medicine and rehabilitation perspective on notalgia paresthetica diagnosis and treatment. This article presents a case report of a 39-yr-old woman with pain, pruritus, and a hyperpigmented area in the right dorsal infra scapular region. The diagnosis of notalgia paresthetica was established. She was successfully treated with topical anesthetics, postural corrective exercises, scapular muscle strengthening, and pectoral muscle stretching. In this context, different treatment options were reviewed. A small set of pharmacological and nonpharmacological techniques were identified. Several of these modalities belong to the physical medicine and rehabilitation field of action.
Notalgia paresthetica is a rarely reported T2–T6 sensory neuropathy whose etiology and treatment are not fully established. Although it is believed to be common in dermatological practice, it remains underrecognized, underdiagnosed, and therefore underreported. This case-report provides a physical medicine and rehabilitation perspective on notalgia paresthetica diagnosis and treatment. This article presents a case report of a 39-yr-old woman with pain, pruritus, and a hyperpigmented area in the right dorsal infra scapular region. The diagnosis of notalgia paresthetica was established. She was successfully treated with topical anesthetics, postural corrective exercises, scapular muscle strengthening, and pectoral muscle stretching. In this context, different treatment options were reviewed. A small set of pharmacological and nonpharmacological techniques were identified. Several of these modalities belong to the physical medicine and rehabilitation field of action.https://ift.tt/2Bcgijh
Onabotulinum Toxin A Injections Into the Salivary Glands for Spinal Muscle Atrophy Type I: A Prospective Case Series of 4 Patients
 Objective The aim of the study was to investigate the safety and efficacy of onabotulinum toxin A injection to the salivary glands under ultrasound guidance for the treatment of sialorrhea in patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I. Design Prospective case series with four patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I who received onabotulinum toxin A injection to parotid and submandibular glands for sialorrhea as part of clinical care. All four patients received validated surveys for measuring drooling, including objective measures of number of bib changes, and number of mouth wipes before injection and 4–6 wks after injection. Research was limited to survey completion. Scales included the Drooling Severity and Frequency Scale and the Drooling Impact Scale as well as a new scale used in our clinic, the Posterior Drooling Scales looking at coughing/choking and number of aspiration pneumonias. Results There were no adverse events. All four patients showed clinically significant improvements. The improvement in drooling using the Drooling Impact Scale was statistically significant (paired t test, t = 3.243, P = 0.048). All patients improved with number of mouth wipes. Conclusion Ultrasound-guided onabotulinum toxin A injections to the salivary glands may be a safe and effective method of decreasing drooling in patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I.
Objective The aim of the study was to investigate the safety and efficacy of onabotulinum toxin A injection to the salivary glands under ultrasound guidance for the treatment of sialorrhea in patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I. Design Prospective case series with four patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I who received onabotulinum toxin A injection to parotid and submandibular glands for sialorrhea as part of clinical care. All four patients received validated surveys for measuring drooling, including objective measures of number of bib changes, and number of mouth wipes before injection and 4–6 wks after injection. Research was limited to survey completion. Scales included the Drooling Severity and Frequency Scale and the Drooling Impact Scale as well as a new scale used in our clinic, the Posterior Drooling Scales looking at coughing/choking and number of aspiration pneumonias. Results There were no adverse events. All four patients showed clinically significant improvements. The improvement in drooling using the Drooling Impact Scale was statistically significant (paired t test, t = 3.243, P = 0.048). All patients improved with number of mouth wipes. Conclusion Ultrasound-guided onabotulinum toxin A injections to the salivary glands may be a safe and effective method of decreasing drooling in patients with spinal muscular atrophy type I.https://ift.tt/2Kbb6z5
Co-morbidities Associated With Early Mortality in Adults With Spina Bifida
 Objective The aims of this quality improvement project were to identify secondary conditions and medical co-morbidities in adult patients with spina bifida and to determine which factors were associated with an earlier age of death. Design Retrospective chart review of 487 patients who attended the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Adult Spina Bifida Clinic between August 1, 2005, and June 6, 2017, was conducted. Results Of 487 patients who had received care at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Adult Spina Bifida Clinic, 48 were deceased. The most commonly reported causes of death included infection, respiratory failure, renal failure, shunt malfunction, and metastatic cancer. Underlying co-morbidities and secondary conditions included hydrocephalus, Chiari II malformation, tethered cord, scoliosis, and abnormal renal function. In deceased patients, earlier age of death was significantly associated with myelomeningocele subtype and the presence of hydrocephalus and Chiari II malformation. Conclusions Clinicians treating individuals with spina bifida should be aware of the potential for earlier mortality in individuals with myelomeningocele, hydrocephalus, and Chiari II malformation, especially with regard to infection, respiratory failure, renal failure, shunt malfunction, and cancer. To Claim CME Credits Complete the self-assessment activity and evaluation online at https://ift.tt/1l80W45 CME Objectives Upon completion of this article, the reader should be able to: (1) Discuss the importance of recognizing co-morbidities in adult individuals with spina bifida; (2) Describe secondary conditions and medical co-morbidities associated with spina bifida; and (3) Identify which conditions are associated with earlier age of death in adult individuals with spina bifida. Level Advanced Accreditation The Association of Academic Physiatrists is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians. The Association of Academic Physiatrists designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should only claim credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
Objective The aims of this quality improvement project were to identify secondary conditions and medical co-morbidities in adult patients with spina bifida and to determine which factors were associated with an earlier age of death. Design Retrospective chart review of 487 patients who attended the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Adult Spina Bifida Clinic between August 1, 2005, and June 6, 2017, was conducted. Results Of 487 patients who had received care at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Adult Spina Bifida Clinic, 48 were deceased. The most commonly reported causes of death included infection, respiratory failure, renal failure, shunt malfunction, and metastatic cancer. Underlying co-morbidities and secondary conditions included hydrocephalus, Chiari II malformation, tethered cord, scoliosis, and abnormal renal function. In deceased patients, earlier age of death was significantly associated with myelomeningocele subtype and the presence of hydrocephalus and Chiari II malformation. Conclusions Clinicians treating individuals with spina bifida should be aware of the potential for earlier mortality in individuals with myelomeningocele, hydrocephalus, and Chiari II malformation, especially with regard to infection, respiratory failure, renal failure, shunt malfunction, and cancer. To Claim CME Credits Complete the self-assessment activity and evaluation online at https://ift.tt/1l80W45 CME Objectives Upon completion of this article, the reader should be able to: (1) Discuss the importance of recognizing co-morbidities in adult individuals with spina bifida; (2) Describe secondary conditions and medical co-morbidities associated with spina bifida; and (3) Identify which conditions are associated with earlier age of death in adult individuals with spina bifida. Level Advanced Accreditation The Association of Academic Physiatrists is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education to provide continuing medical education for physicians. The Association of Academic Physiatrists designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should only claim credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.https://ift.tt/2BcVWXe
Improvement During Inpatient Rehabilitation Among Older Adults With Guillain-Barré Syndrome, Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson Disease, and Stroke
 Objective The aim of the study was to quantify the improvement in independence experienced by patients with the following diagnoses: Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, and stroke after inpatient rehabilitation. Design Subjects who were admitted to inpatient rehabilitation hospitals in 2012–2013 with an incident diagnosis of the following: Guillain-Barré syndrome (n = 1079), multiple sclerosis (n = 1438), Parkinson disease (n = 11,834), or stroke (n = 131,313), were included. The main outcome measure was improvement in Functional Independence Measure scores on self-care, mobility, and cognition during inpatient rehabilitation. We estimated percent improvement from a linear mixed-effects model adjusted for patients' age, sex, race/ethnicity, comorbidity count, diagnostic group (Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, and stroke), and admission score. Results All patient diagnostic groups receiving inpatient rehabilitation improved across all three domains. The largest adjusted percent improvements were observed in the mobility domain and the smallest in the cognition domain for all groups. Percent improvement in mobility ranged from 84.9% (multiple sclerosis) to 144.0% (Guillain-Barré syndrome), self-care from 49.5% (multiple sclerosis) to 84.1% (Guillain-Barré syndrome), and cognition from 34.0% (Parkinson disease) to 51.7% (Guillain-Barré syndrome). Patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome demonstrated the greatest percent improvement across all three domains. Conclusions Patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, and stroke should improve during inpatient rehabilitation but anticipated outcomes for patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome should be even higher.
Objective The aim of the study was to quantify the improvement in independence experienced by patients with the following diagnoses: Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, and stroke after inpatient rehabilitation. Design Subjects who were admitted to inpatient rehabilitation hospitals in 2012–2013 with an incident diagnosis of the following: Guillain-Barré syndrome (n = 1079), multiple sclerosis (n = 1438), Parkinson disease (n = 11,834), or stroke (n = 131,313), were included. The main outcome measure was improvement in Functional Independence Measure scores on self-care, mobility, and cognition during inpatient rehabilitation. We estimated percent improvement from a linear mixed-effects model adjusted for patients' age, sex, race/ethnicity, comorbidity count, diagnostic group (Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, and stroke), and admission score. Results All patient diagnostic groups receiving inpatient rehabilitation improved across all three domains. The largest adjusted percent improvements were observed in the mobility domain and the smallest in the cognition domain for all groups. Percent improvement in mobility ranged from 84.9% (multiple sclerosis) to 144.0% (Guillain-Barré syndrome), self-care from 49.5% (multiple sclerosis) to 84.1% (Guillain-Barré syndrome), and cognition from 34.0% (Parkinson disease) to 51.7% (Guillain-Barré syndrome). Patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome demonstrated the greatest percent improvement across all three domains. Conclusions Patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, and stroke should improve during inpatient rehabilitation but anticipated outcomes for patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome should be even higher.https://ift.tt/2BdUSSZ
The Effect of Stabilization Exercises on Pain, Disability, and Pelvic Floor Muscle Function in Postpartum Lumbopelvic Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Objective The effect of stabilization exercises on pain, disability, and pelvic floor muscle function in postpartum lumbopelvic pain. Design This is a single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Setting This study was performed at the physiotherapy clinic, Zahedan University of Medical Science, from January to November 2017. Participants Thirty-six multiparous women with persistent postpartum lumbopelvic pain were recruited at least 3 mos after delivery. Interventions Subjects in the training group (n = 18) received electrotherapy modalities and specific stabilizing exercises. The control group (n = 18) received only electrotherapy modalities. Main Outcome Measures Pain, disability, and bladder base displacement (at rest and pelvic floor muscles contraction) were measured through visual analog scale, Oswestry Disability Index questionnaires, and transabdominal ultrasound imaging respectively at baseline and after 6 wks of intervention. Results Between-groups comparison showed significant improvement in pain, disability, and bladder base displacement in the training group (P
Objective The effect of stabilization exercises on pain, disability, and pelvic floor muscle function in postpartum lumbopelvic pain. Design This is a single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Setting This study was performed at the physiotherapy clinic, Zahedan University of Medical Science, from January to November 2017. Participants Thirty-six multiparous women with persistent postpartum lumbopelvic pain were recruited at least 3 mos after delivery. Interventions Subjects in the training group (n = 18) received electrotherapy modalities and specific stabilizing exercises. The control group (n = 18) received only electrotherapy modalities. Main Outcome Measures Pain, disability, and bladder base displacement (at rest and pelvic floor muscles contraction) were measured through visual analog scale, Oswestry Disability Index questionnaires, and transabdominal ultrasound imaging respectively at baseline and after 6 wks of intervention. Results Between-groups comparison showed significant improvement in pain, disability, and bladder base displacement in the training group (Phttps://ift.tt/2BcIhPD
State of the States: Growing PhysiatryAssociation of Academic Physiatrists Position Statement Addressing Academic Physiatry and Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Growth
 The growth of physiatry in the United States is dependent on academic exposure at both the undergraduate and graduate medical education levels. Undergraduate medical education provides students with knowledge of physiatry, as well as proper understanding of human function, medical rehabilitation treatments, and of physiatrists as consultants. Graduate medical education contributes more directly to the total number of practicing physiatrists. This article presents disparities in medical student exposure to physiatry, physical medicine and rehabilitation residency positions, the number of practicing physiatrists, and physical medicine and rehabilitation–relevant patient care needs, by state. In the model, these disparities are highlighted to provide guidance and expose gaps/opportunities for targeted physiatric growth.
The growth of physiatry in the United States is dependent on academic exposure at both the undergraduate and graduate medical education levels. Undergraduate medical education provides students with knowledge of physiatry, as well as proper understanding of human function, medical rehabilitation treatments, and of physiatrists as consultants. Graduate medical education contributes more directly to the total number of practicing physiatrists. This article presents disparities in medical student exposure to physiatry, physical medicine and rehabilitation residency positions, the number of practicing physiatrists, and physical medicine and rehabilitation–relevant patient care needs, by state. In the model, these disparities are highlighted to provide guidance and expose gaps/opportunities for targeted physiatric growth.https://ift.tt/2Kelrdy
Association of Admission Functional Status and Assistive Device Provision for Veterans Poststroke: A Retrospective Study
 Objectives The aims of the study were (a) to provide knowledge about the provision of assistive devices in practice and (b) to describe the challenges of standardizing device provision. Design This is a retrospective study using Department of Veteran Affairs National Prosthetic Patient Database and other administrative databases. The cohort included all veterans treated by the Veterans Health Administration for stroke during fiscal years 2007–2008. Descriptive methods were used to analyze data with emphasis on inspecting relationships between device provision and motor and cognitive function using Functional Independence Measure scores. Results A total of 8374 veterans treated for stroke and receiving at least one assistive device are included. Individuals who received standard or caregiver controlled wheelchairs tended to be older, and those who received ultralight or caregiver controlled wheelchairs had a higher proportion of Hispanics than the overall cohort. Veterans who received any type of wheelchair had lower motor, cognitive, and total functioning scores than the cohort as a whole. Veterans who received canes had the highest functioning. Veteran patients who received patient lifts and beds had lower cognitive scores compared with the overall cohort. Conclusions Functional status can provide some objectivity to the largely subjective assistive device provision decision-making process; however, many other factors must be considered simultaneously, complicating efforts to standardize provision.
Objectives The aims of the study were (a) to provide knowledge about the provision of assistive devices in practice and (b) to describe the challenges of standardizing device provision. Design This is a retrospective study using Department of Veteran Affairs National Prosthetic Patient Database and other administrative databases. The cohort included all veterans treated by the Veterans Health Administration for stroke during fiscal years 2007–2008. Descriptive methods were used to analyze data with emphasis on inspecting relationships between device provision and motor and cognitive function using Functional Independence Measure scores. Results A total of 8374 veterans treated for stroke and receiving at least one assistive device are included. Individuals who received standard or caregiver controlled wheelchairs tended to be older, and those who received ultralight or caregiver controlled wheelchairs had a higher proportion of Hispanics than the overall cohort. Veterans who received any type of wheelchair had lower motor, cognitive, and total functioning scores than the cohort as a whole. Veterans who received canes had the highest functioning. Veteran patients who received patient lifts and beds had lower cognitive scores compared with the overall cohort. Conclusions Functional status can provide some objectivity to the largely subjective assistive device provision decision-making process; however, many other factors must be considered simultaneously, complicating efforts to standardize provision.https://ift.tt/2BdFuGa
Efficacy of Compression Gloves in the Rehabilitation of Distal Radius Fractures: Randomized Controlled Study
 Objective The aim of this study was to examine the outcomes of wearing made-to-measure compression gloves after distal radius fracture. Design In a randomized controlled trial, adults who were about 6 wks post distal radius fracture were recruited and divided into a comparison control group (n = 15), who received standard rehabilitation twice a week for half an hour, and an intervention group (n = 17), who additionally used compression gloves. All treatments were conducted at a single rehabilitation clinic. Outcomes assessed were wrist and finger range of motion, grip strength, swelling, pain, and activities of daily living (using the Patient Rating Wrist Evaluation). The intervention group underwent additional objective dynamic assessments of range of motion with and without the gloves. Results The intervention group demonstrated reduced swelling, pain, and analgesic use; increased wrist range of motion; better scores for specific hand functions; and greater participation in activities of daily living compared with the comparison group. Conclusion This randomized controlled trial shows that using compression gloves during the rehabilitation phase after distal radius fracture improves daily functioning and reduces adverse symptoms. These improvements, which are important in their own right, are also expected to aid in preventing the development of chronic conditions and disability. Evidence Level II Un-blinded prospective comparative study.
Objective The aim of this study was to examine the outcomes of wearing made-to-measure compression gloves after distal radius fracture. Design In a randomized controlled trial, adults who were about 6 wks post distal radius fracture were recruited and divided into a comparison control group (n = 15), who received standard rehabilitation twice a week for half an hour, and an intervention group (n = 17), who additionally used compression gloves. All treatments were conducted at a single rehabilitation clinic. Outcomes assessed were wrist and finger range of motion, grip strength, swelling, pain, and activities of daily living (using the Patient Rating Wrist Evaluation). The intervention group underwent additional objective dynamic assessments of range of motion with and without the gloves. Results The intervention group demonstrated reduced swelling, pain, and analgesic use; increased wrist range of motion; better scores for specific hand functions; and greater participation in activities of daily living compared with the comparison group. Conclusion This randomized controlled trial shows that using compression gloves during the rehabilitation phase after distal radius fracture improves daily functioning and reduces adverse symptoms. These improvements, which are important in their own right, are also expected to aid in preventing the development of chronic conditions and disability. Evidence Level II Un-blinded prospective comparative study.https://ift.tt/2Bb8Rsn
Bone Marrow Fat Physiology in Relation to Skeletal Metabolism and Cardiometabolic Disease Risk in Children With Cerebral Palsy
 Individuals with cerebral palsy exhibit neuromuscular complications and low physical activity levels. Adults with cerebral palsy exhibit a high prevalence of chronic diseases, which is associated with musculoskeletal deficits. Children with cerebral palsy have poor musculoskeletal accretion accompanied by excess bone marrow fat, which may lead to weaker bones. Mechanistic studies to determine the role of bone marrow fat on skeletal growth and maintenance and how it relates to systemic energy metabolism among individuals with cerebral palsy are lacking. In this review, we highlight the skeletal status in children with cerebral palsy and analyze the existing literature on the interactions among bone marrow fat, skeletal health, and cardiometabolic disease risk in the general population. Clinically vital questions are proposed, including the following: (1) Is the bone marrow fat in children with cerebral palsy metabolically distinct from typically developing children in terms of its lipid and inflammatory composition? (2) Does the bone marrow fat suppress skeletal acquisition? (3) Or, does it accelerate chronic disease development in children with cerebral palsy? (4) If so, what are the mechanisms? In conclusion, although inadequate mechanical loading may initiate poor skeletal development, subsequent expansion of bone marrow fat may further impede skeletal acquisition and increase cardiometabolic disease risk in those with cerebral palsy.
Individuals with cerebral palsy exhibit neuromuscular complications and low physical activity levels. Adults with cerebral palsy exhibit a high prevalence of chronic diseases, which is associated with musculoskeletal deficits. Children with cerebral palsy have poor musculoskeletal accretion accompanied by excess bone marrow fat, which may lead to weaker bones. Mechanistic studies to determine the role of bone marrow fat on skeletal growth and maintenance and how it relates to systemic energy metabolism among individuals with cerebral palsy are lacking. In this review, we highlight the skeletal status in children with cerebral palsy and analyze the existing literature on the interactions among bone marrow fat, skeletal health, and cardiometabolic disease risk in the general population. Clinically vital questions are proposed, including the following: (1) Is the bone marrow fat in children with cerebral palsy metabolically distinct from typically developing children in terms of its lipid and inflammatory composition? (2) Does the bone marrow fat suppress skeletal acquisition? (3) Or, does it accelerate chronic disease development in children with cerebral palsy? (4) If so, what are the mechanisms? In conclusion, although inadequate mechanical loading may initiate poor skeletal development, subsequent expansion of bone marrow fat may further impede skeletal acquisition and increase cardiometabolic disease risk in those with cerebral palsy.https://ift.tt/2BcI7rv
MGMT Testing in Glioblastomas: Pitfalls and Opportunities
https://ift.tt/2DpoVse
Use of polygenic risk scores of nicotine metabolism in predicting smoking behaviors
Pharmacogenomics, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2PyNWIR
A review discussing the use of polyethylene glycol microspheres in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
Future Oncology, Ahead of Print.
https://ift.tt/2QQ91e8
Evaluation of 0.2% delmopinol mouth rinse for prevention of peri‐implant mucositis and peri‐implantitis: A randomized controlled canine study
Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the effectiveness of 0.2% delmopinol mouth rinse in maintenance of peri‐implant tissue health and prevention or inhibition of peri‐implant mucositis and peri‐implantitis.
Materials and Methods
Four weeks following tooth extraction, eight titanium dental implants, were placed in six dogs' mandibles. Three dogs were assigned to the test or placebo mouth rinse. Eight weeks following implant installation (T2) ligature was placed to induce peri‐implant disease. Clinical and radiographic assessment was performed during the study period as well as micro‐CT analysis and histologic assessment to evaluate Bone‐Implant Contact at the end of the follow‐up (T4).
Results
Plaque at implant sites before ligature placement (T2) was lower for the test group (0.7 ± 1.0 vs 1.5 ± 1.3, P < .05). The ratio of affected implant (PD ≧4 mm) at T2 and T4 in the test group was significantly smaller than that of the placebo group (T2, 17% vs 47%, P < .01; T4, 67% vs 83%, P < .05). The test agent also seemed to be effective in partially preventing bone loss induced by ligature placement according to the Computed Tomography and histologic analysis (test, 1.1 ± 0.8 mm; placebo, 1.5 ± 0.9 mm).
Conclusions
Within the limits of this animal model study, the results of the study indicate that the 0.2% delmopinol rinse might play a role in prevention of peri‐implant disease development.
https://ift.tt/2zdm6Yi
SEOM clinical guidelines for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (2018)
Abstract
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for up to 85% of all lung cancers. The last few years have seen the development of a new staging system, diagnostic procedures such as liquid biopsy, treatments like immunotherapy, as well as deeper molecular knowledge; so, more options can be offered to patients with driver mutations. Groups with specific treatments account for around 25% and demonstrate significant increases in overall survival, and in some subgroups, it is important to evaluate each treatment alternative in accordance with scientific evidence, and even more so with immunotherapy. New treatments similarly mean that we must reconsider what should be done in oligometastatic disease where local treatment attains greater value.
https://ift.tt/2OOB77Y
Understanding Moment‐to‐Moment Processing of Visual Narratives
Abstract
What role do moment‐to‐moment comprehension processes play in visual attentional selection in picture stories? The current work uniquely tested the role of bridging inference generation processes on eye movements while participants viewed picture stories. Specific components of the Scene Perception and Event Comprehension Theory (SPECT) were tested. Bridging inference generation was induced by manipulating the presence of highly inferable actions embedded in picture stories. When inferable actions are missing, participants have increased viewing times for the immediately following critical image (Magliano, Larson, Higgs, & Loschky, #cogs12699-bib-0074). This study used eye‐tracking to test competing hypotheses about the increased viewing time: (a) Computational Load: inference generation processes increase overall computational load, producing longer fixation durations; (b) Visual Search: inference generation processes guide eye‐movements to pick up inference‐relevant information, producing more fixations. Participants had similar fixation durations, but they made more fixations while generating inferences, with that process starting from the fifth fixation. A follow‐up hypothesis predicted that when generating inferences, participants fixate scene regions important for generating the inference. A separate group of participants rated the inferential‐relevance of regions in the critical images, and results showed that these inferentially relevant regions predicted differences in other viewers' eye movements. Thus, viewers' event models in working memory affect visual attentional selection while viewing visual narratives.
https://ift.tt/2PzMaHo
Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy: Risk Factors, Biomarkers and Prevention
Abstract
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is one of the most important direct epilepsy‐related causes of death, with an incidence in adults of 1.2 per 1000 person years. Generalized tonic‐clonic seizures have consistently emerged as the leading risk factor for SUDEP, particularly when such seizures are uncontrolled. High seizure burden, lack of antiepileptic drug (AED) treatment, polytherapy, intellectual disability, and prone position at the time of death are other key risk factors. Unfortunately, despite advances in treatment, overall mortality rates in epilepsy are rising. It is imperative that we learn more about SUDEP so that effective prevention strategies can be implemented. To help identify persons at greater risk of SUDEP and in need of closer monitoring, biomarkers are needed. Candidate biomarkers include electrocardiographic, electroencephalographic, and imaging abnormalities observed more frequently in those who have died suddenly and unexpectedly. As our knowledge of the pathophysiologic mechanisms behind SUDEP have increased, various preventative measures have been proposed. These include lattice pillows, postictal oxygen therapy, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and inhibitors of opiate and adenosine receptors. Unfortunately, no randomized clinical trials are available to definitively conclude these measures are effective. Rather, gaining the best control of seizures possible (with AEDs, devices, and resective surgery) still remains the intervention with the best evidence to reduce the risk of SUDEP. In this evidenced‐based review, we explore the incidence of SUDEP and review the risk factors, biomarkers, and latest prevention strategies.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
https://ift.tt/2QO7HbL
Endoscopic ultrasound‐guided choledochoduodenostomy using a thin stent delivery system in patients with unresectable malignant distal biliary obstruction: a prospective multicenter study
Abstract
Objectives
When endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) fails in patients with malignant distal biliary obstruction, endoscopic ultrasound‐guided choledochoduodenostomy (EUS‐CDS) is an alternative. It associates with high technical and clinical success rates but also high adverse events rates. This prospective cohort study was aimed to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of EUS‐CDS with our newly developed partially‐covered self‐expandable metal stent with a thin delivery system.
Methods
The patients consisted of all consecutive patients in three tertiary referral centers with unresectable malignant distal obstruction in whom ERCP failed and in whom EUS‐CDS with the thin delivery system was selected as the second‐line approach. The rates of clinical success, technical success, technical success in cases not requiring fistulous tract dilation, adverse events, and stent dysfunction were determined.
Results
In the 20 patients, the technical and clinical success rates were 95.0% (19/20) and 100% (19/19), respectively. In 31.6% (6/19), the delivery system was successfully inserted into the bile duct without requiring a fistulous‐tract dilatation device. These patients had significantly shorter procedure times than patients requiring fistulous‐tract dilatation (12.7±3.1 vs. 23.2±2.1 min; P<0.01). One patient (5.0%) who required fistulous dilation had an adverse event, which was managed conservatively. There were no procedure‐related deaths. During follow‐up, four patients (21.1%) developed stent dysfunction. Re‐intervention was successful in all cases.
Conclusions
The EUS‐CDS approach was associated with 95% technical and 100% clinical success rates, with adverse events reported in 5% of cases. EUS‐CDS may become safer if efforts are made to avoid the dilation step (UMIN 000023938).
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
https://ift.tt/2Q1xPCN
Endoscopic radiofrequency biliary ablation treatment: a comprehensive review
Abstract
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) acts by delivering thermal energy within the tissue, the result of a high‐frequency alternating current released from an active electrode, leading to coagulative necrosis and cellular death. Recently, a biliary catheter working on a guide‐wire has been developed and a number of studies have been performed so far. The present paper provides a comprehensive review of the literature on the results of the use of RFA for the clinical management of patients with unresectable malignant biliary strictures, benign biliary strictures, and residual adenomatous tissue in the bile duct after endoscopic papillectomy.
The available data show that biliary RFA treatment is a promising adjuvant therapy in patients with unresectable malignant biliary obstruction. The procedure is safe, well tolerated and improves stent patency and survival, even though more studies are warranted. In patients with residual endobiliary adenomatous tissue after endoscopic papillectomy, a significant rate of neoplasia eradication after a single RFA session has been reported, thus favoring this treatment over surgical intervention. In these patients, as well as, in those with benign biliary strictures, dedicated probes with a short electrode able to focus the RF current on the short stenosis are needed to expand RFA treatment for these indications.
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
https://ift.tt/2Ds3UwQ
Use it or lose it? Effects of age, experience, and disuse on crawling
Abstract
What happens to early acquired but later abandoned motor skills? To investigate effects of disuse on early‐developing motor skills, we examined crawling in two groups of habitual crawlers (34 6–12‐month‐old infants and five adults with Uner Tan Syndrome) and two groups of rusty crawlers (27 11–12‐year‐old children and 13 college‐aged adults). Habitual crawlers showed striking similarities in gait patterns, limbs supporting the body, and crawling speed, despite dramatic differences in crawling practice, posture, and body size. Habitual crawlers trotted predominantly, whereas rusty crawlers showed a variety of gait patterns. Within sequences, habitual crawlers and children showed more switches in gait patterns than young adults. Children crawled faster and kept fewer limbs on the grounds than the other groups. Old crawling patterns were retained despite disuse, but new ones were also added. Surprisingly, results indicate that nothing was lost with disuse, but some features of crawling were gained or altered.
https://ift.tt/2Q7GR14
Cortisol secretion moderates the association between mother–infant attachment at 17 months and child behavior at age 5 years
Abstract
This study examined infant cortisol secretion as a moderator of the association between mother–infant attachment security at age 17 months and child behavior at age 5 years. A longitudinal community sample of 96 mother–child dyads participated in the strange situation procedure (SSP) at age 17 months. Cortisol was collected at baseline, and at 20 and 40 min post‐SSP. Maternal reports of child behavior were collected at age 5 years. Results revealed that the associations between nonsecure mother–infant attachment and higher total, internalizing, and externalizing behavior were stronger for infants with high cortisol secretion, relative to infants with low cortisol secretion. The model of interaction differed depending on the outcome, with diathesis‐stress explaining variance in total as well as internalizing behavior, and with differential susceptibility explaining variance in externalizing behavior. These findings augment our understanding of risk and resilience to the impact of the early rearing environment on later psychopathology.
https://ift.tt/2DqaP9W
NMT1 inhibition modulates breast cancer progression through stress-triggered JNK pathway
NMT1 inhibition modulates breast cancer progression through stress-triggered JNK pathway
NMT1 inhibition modulates breast cancer progression through stress-triggered JNK pathway, Published online: 16 November 2018; doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1201-x
NMT1 inhibition modulates breast cancer progression through stress-triggered JNK pathwayhttps://ift.tt/2QL0ERb
The influence of the nylon balloon stiffness on the efficiency of the intra‐aortic balloon occlusion
Summary
In interventional procedures the balloon inflation is used to occlude the artery and thus reduce bleeding. There is no practically accepted measure of the procedure efficiency. A finite element method model with state of the art modelling techniques was built in order to predict the occlusions levels under the influence of different balloon inflation and its material stiffness. The geometries of a healthy human thoracic aorta and an occlusion balloon were idealized. The non‐linear constitutive material of Gasser‐Ogden‐Holzapfel model was employed for the thoracic aorta, the balloon was model as the hyperelastic model. The realistic physiological blood pressure and the balloon inflation pressures were applied to simulate the different occlusions levels. The final outcome shows an important influence of the material stiffness on the balloon deformation and thus the occlusion efficiency.
https://ift.tt/2Q7EwDk
Suicide with an unusual home-manufactured firearm
Abstract
A 22-year-old male with a medical history of depression was found lying on his right side with a pool of blood around his head. A pistol-shaped metal device was found next to the right hand of the deceased. Examination of the body revealed the presence of a gunshot wound to the head. The entrance wound was located in the right temporal area and was partially surrounded by a semicircular muzzle imprint. Analysis of the firearm revealed a home-manufactured device constructed from the posterior part of a captive bolt gun chamber containing a firing pin. The front part of an original captive bolt's cylinder was replaced with a conical iron tube, which could be detached from the chamber by an unscrewing action. The tube was unrifled and drilled in order to accept standard 9 mm ammunition. A hollow rectangular piece of metal was welded to the posterior part of the chamber perpendicularly and used as a grip. Cases of injuries caused by different types of captive bolt guns are well documented in the forensic literature. However, conversions of captive bolts in projectile-discharging devices or their use in the construction of zip guns, as well as the injuries produced by such types of firearms, are extremely rare in forensic and medico-legal practice.
https://ift.tt/2qSlaUM
Cancer immunotherapy of patients with HIV infection
Abstract
Cancer immunotherapy with antibodies against immune checkpoints has made impressive advances in the last several years. The most relevant drugs target programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) expressed on T cells or its ligand, the programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), expressed on cancer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4). Unfortunately, cancer patients with HIV infection are usually excluded from cancer clinical trials, because there are concerns about the safety and the anti-tumoral activity of these novel therapies in patients with HIV infection. Several retrospective studies and some case reports now support the notion that antibodies against immune checkpoints are safe and active in cancer patients with HIV infection, but prospective data in these patients are lacking. In addition, signs of antiviral activity with increase in CD4 T cell counts, plasma viremia reduction or decrease in the viral reservoir have been reported in some of the patients treated, although no patient achieved a complete clearance of the viral reservoir. Here we briefly summarize all clinical cases reported in the literature, as well as ongoing clinical trials testing novel immunotherapy drugs in cancer patients with HIV infection.
https://ift.tt/2BcvyMN
Bridging the gap between vaccination with Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) and immunological tolerance: the cases of type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis
Giovanni Ristori | Denise Faustman | Giuseppe Matarese | Silvia Romano | Marco Salvetti
https://ift.tt/2qS6J2I
Two MYC Homology Boxes Drive Tumorigenesis [Research Watch]
A protein interaction screen reveals 336 MYC-binding proteins that bind to distinct MYC homology boxes (MB).
https://ift.tt/2qPzFbX
A Developed STING Agonist Has Systemic Antitumor Activity [Research Watch]
A dimeric amidobenzimidazole (diABZI) STING agonist enhances adaptive immunity and antitumor activity.
https://ift.tt/2FoXDot
Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma in an adult with Proteus syndrome. First re-ported case
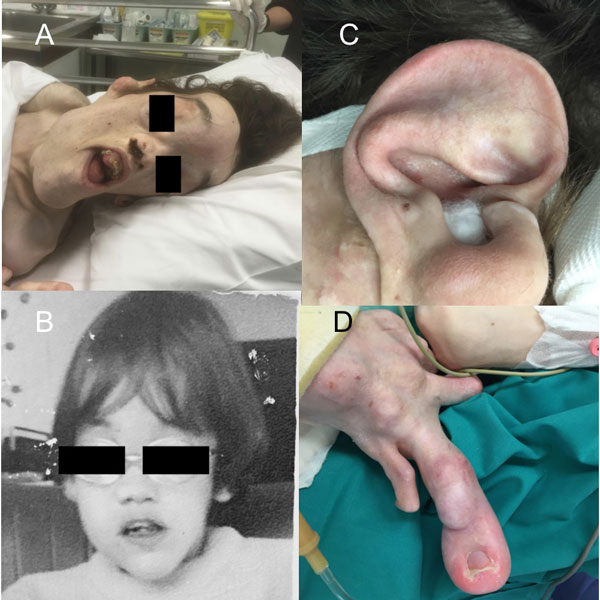
CASE REPORT
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):147-149
Delides A1, PanayiotidesJG2, Kaberos A3, Giotakis I1
12nd Otolaryngology Department, "Attikon" University Hospital, 22nd Department of Pathology, "Attikon" University Hospital, School of Medicine, National & Kapodistrian University of Athens, 3Otolaryngology Department, "Jannio" Hospital of Peireaus, Athens, Greece
https://ift.tt/2FoOY5d
Exercise testing and adipokine levels for the evaluation of overweight and obesity in children
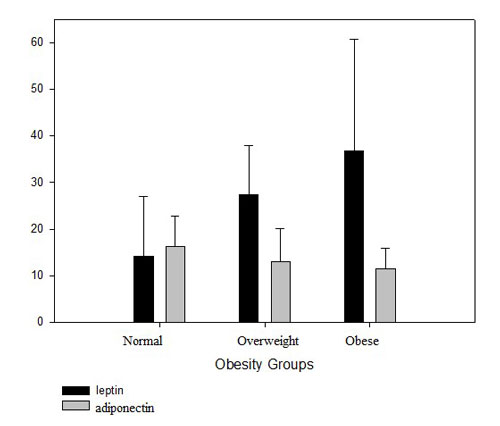
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):124-129
Tsiroukidou K1, Papagianni M1, Hatziagorou E1, Galli-Tsinopoulou A2, Giannopoulos A3, Tsanakas I1
13rd Department of Pediatrics, Hippokration General Hospital, 24th Department of Pediatrics, Papageorgiou General Hospital, 32nd Department of Pediatrics, AHEPA University General Hospital, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
e
https://ift.tt/2FqRNTn
Thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in invasive and non-invasive urothelial carcinomas
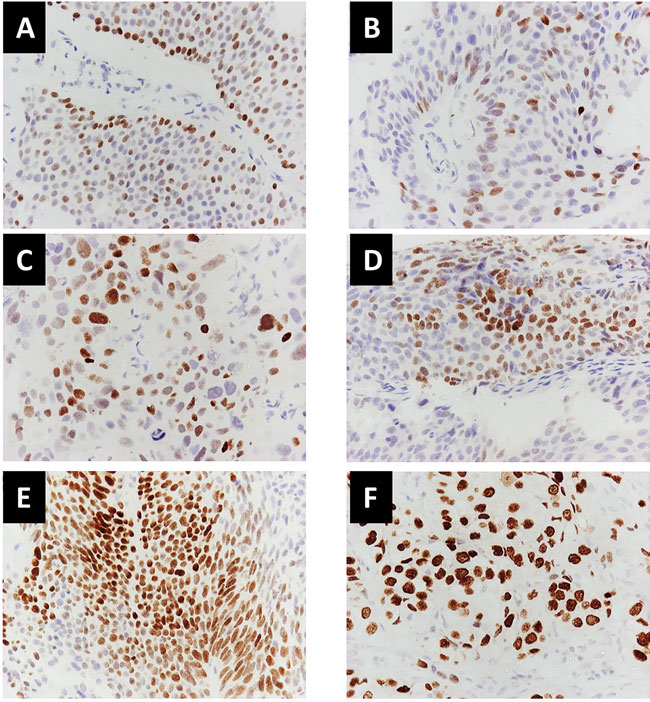
CASE SERIES
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):154-157
Sotiriou S1, Koletsas N2, Koletsa T1, Touloupidis S3, Lambropoulou M4
1Pathology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 2Urology Department, Interbalkan Medical Center, Thessaloniki, 3Urology Department, 4Laboratory of Histology-Embryology, School of Medicine, Democritus University of Thrace, Alexandroupolis, Greece
https://ift.tt/2qTrxH7
Caregiver’s perception of epilepsy treatment, quality of life and comorbidi-ties in an international cohort of CDKL5 patients
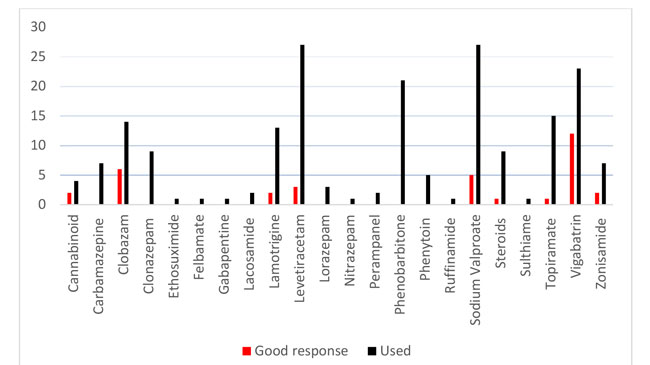
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):130-135
Amin S1, Majumdar A1, Mallick AA1, Patel J1, Scatchard R1, Partridge CA2, Lux A1
1Pediatric Neurology, University Hospitals Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2CDKL5-UK Charity
https://ift.tt/2FB9waK
Understanding neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy with metabolomics
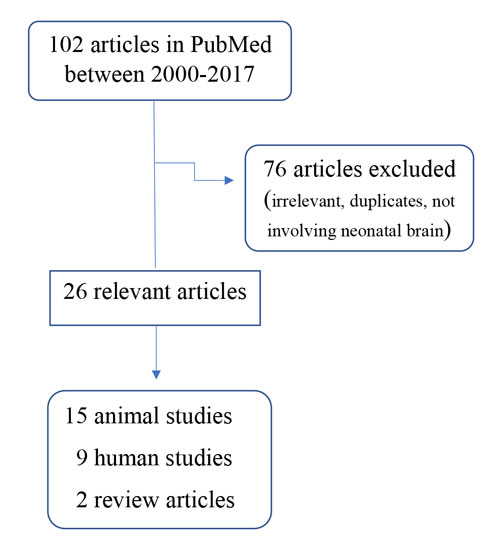
REVIEW ARTICLE
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3 ):115-123
Efstathiou N1, Theodoridis G2, Sarafidis K1
11st Department of Neonatology, School of Medicine, 2School of Chemistry, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
https://ift.tt/2qSPApT
Matrix metalloproteinases in ureteropelvic junction obstruction
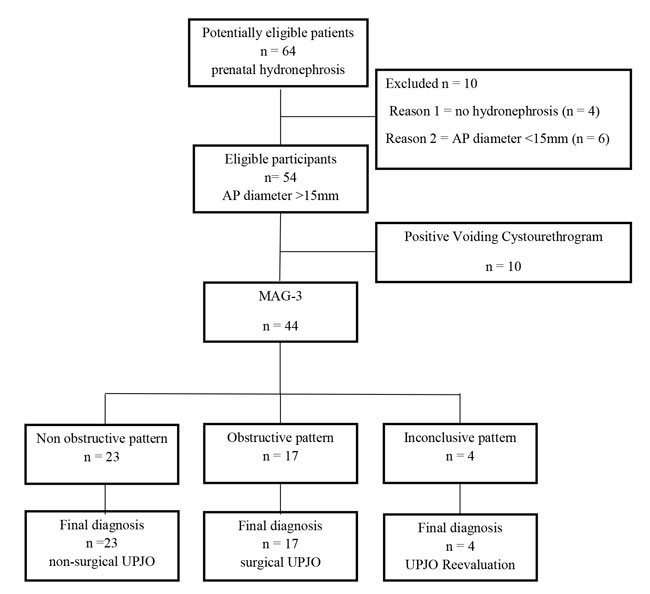
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):136-139
Pavlaki A, Printza N, Farmaki E, Stabouli S, Taparkou A, Dotis J, Papachristou F
First Department of Pediatrics, Hippokratio Hospital, School of Medicine, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
https://ift.tt/2FmEjIm
Isolated sphenochoanal polyp: report of three cases
CASE REPORT
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):150-153
Çeçen A1, Kemal O2, Atmaca S2, Kavaz E2
1Department of Otolaryngology, Samsun Education and Reserch Hospital, 2Department of Otolaryngology, Ondokuz Mayıs University School of Medicine, Samsun, Turkey
https://ift.tt/2qSaeGE
Endovascular treatment of an axillary artery pseudoaneurysm following shoulder arthroplasty
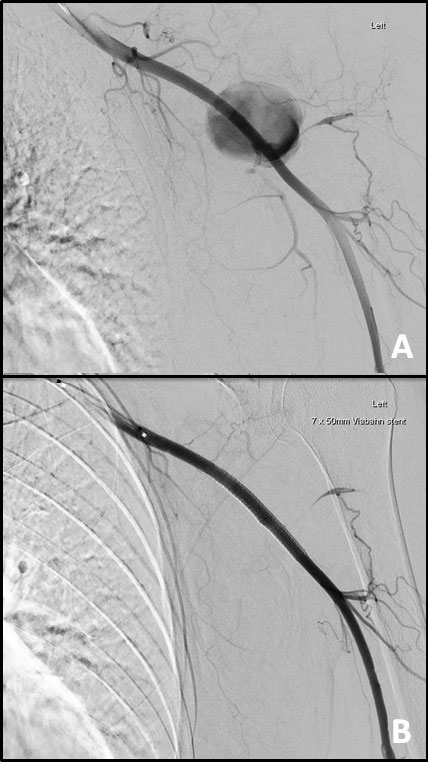
LETTER
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):158
Katsogridakis E, Greaves N, Murray D
Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK
https://ift.tt/2qOyOIe
Syncope in a patient with tortuous right common carotid artery
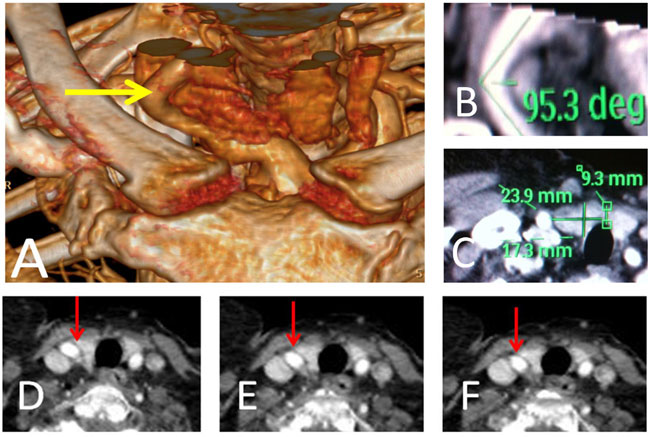
LETTER
Hippokratia 2017, 21(3):160
Katsanos S, Katogiannis K, Parissis J
Department of Emergency Medicine, "Attikon" University Hospital, Athens, Greece
https://ift.tt/2qSsfES
Soft Tissue Disorders of the Mouth
Soft tissue disorders of the mouth encompass a wide expanse of pathophysiology. This article focuses on the identification, etiology, management, and complications of common infectious processes (candidiasis, dental caries, and herpes labialis), inflammatory lesions (sialolithiasis, oral lichen planus, and aphthous ulcer), and benign entities (bony tori and mucocele).
https://ift.tt/2PvEA0p
Tracheostomy Emergencies
Tracheostomy is a common procedure for long-term airway management. Although the overall complication rate is greater than 50%, the incidence of serious complications is low. These serious complications can, however, lead to significant morbidity and mortality and it is incumbent on the emergency provider to be prepared to deal with such tracheostomy-related emergencies. The greatest life threats to the tracheostomy patient are decannulation, obstruction, and hemorrhage. Other important but lower-acuity complications include tracheoesophageal fistula formation, tracheal stenosis, infection, and tracheocutaneous fistula formation.
https://ift.tt/2Pzx1Wv
Dental Emergencies
Dental emergencies present frequently to the emergency department and urgent care centers. Trauma to the teeth includes fractures, luxations, and avulsions, which can be reduced in most cases. Avulsed primary teeth should never be replaced. Mouthguards should be worn in most youth sports to prevent many dental injuries. Dental caries can progress to worsening infection and should be diagnosed and promptly referred. More severe infections may require antibiotics, imaging, or incision and drainage. Dental blocks can assist with analgesia and patient comfort during other procedures.
https://ift.tt/2PzQypy
Peripheral Vertigo
This article summarizes the systematic assessment of the dizzy patient who presents with peripheral vertigo. It demonstrates the steps and tests necessary using the Triage-Timing-Trigger–Test (Triage + TiTraTe) method to accurately diagnose the underlying most probable cause while ruling out life-threatening causes. Using video support and just-in-time infographics, it demonstrates the Dix-Hallpike, Semont, Epley, and HINTS maneuvers.
https://ift.tt/2PvEnu2
Ear, Nose, and Throat Emergencies
EMERGENCY MEDICINE CLINICS OF NORTH AMERICA
https://ift.tt/2QNcSJ5
Ears, Nose, and Throat Emergencies
I just recently completed the painful process of taking my second recertification examination in emergency medicine. The process of reviewing the entire core curriculum of our specialty every 10 years is always an eye-opening process, as I have a chance to review so many aspects of the specialty that have fallen from my "regularly used memory." In the process of this review, I became keenly aware once again of just how much of our specialty resides above the shoulders, yet outside the brain. Unbelievably, the ears, nose, mouth, and throat (the "head holes") account for the fourth most important organ system in terms of numbers of questions on the board exam, following cardiovascular, abdominal/gastrointestinal, and thoracic/respiratory.
https://ift.tt/2QPc1rp
Foreign Bodies of the Ear, Nose and Throat
Foreign bodies to the ear, nose, and throat often can be managed in the emergency department, particularly if the patient offers a history consistent with foreign body and is calm and compliant with the examination and removal attempts. Tips for success include analgesia, adequate visualization, immobilization of the patient's head, dexterity and experience level of the provider, and minimizing attempts at removal. It is critical to recognize the risks involved with certain retained objects (button batteries or sharp objects) and when to call a consultant to help facilitate safe, successful removal of objects to the ear, nose, and throat.
https://ift.tt/2PylGpK
Ear, Nose, and Throat Emergencies
The American Board of Emergency Medicine lists 30 specific Ear, Nose, and Throat disorders as well as five Otolaryngology-specific procedures in its 2016 Model of the Clinical Practice of Emergency Medicine. These disorders and their associated procedural skills range from critical in nature to lower acuity. As such, it is incumbent upon emergency providers to be prepared when these patients present for care. While specialty consultation with an otolaryngologist may be available at some centers, often timely access to such consultation is not possible.
https://ift.tt/2QP2wsa
Sinusitis Update
Rhinosinusitis affects many pediatric patients as well as 1 in 6 adults in any given year, resulting in ambulatory care, pediatric, and emergency department visits. Uncomplicated rhinosinusitis requires no imaging or testing and does not require antibiotic treatment. Using strict clinical diagnostic criteria may minimize unnecessary antibiotics. When indicated, amoxicillin with or without clavulanate for 5 to 10 days remains the first-line antibiotic, despite increasing incidence of staphylococcal sinusitis in the post-pneumococcal conjugate vaccine era. Emergency providers also need to recognize atypical cases in which uncommon but serious complications of sinusitis cause both morbidity and mortality.
https://ift.tt/2PylE16
Erratum
The following errors were found in the article, "Pediatric Sepsis" by Melanie K. Prusakowski and Audrey P. Chen in the Severe Sepsis Care in the Emergency Department issue of Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America (February 2017, Volume 35, Issue 1, p1-240):
https://ift.tt/2QJYiln
Epistaxis
Most anterior epistaxis originates primarily from the Kiesselbach plexus, whereas posterior epistaxis is less common and originates from branches of the sphenopalatine artery. Risk factors include local trauma, foreign body insertion, substance abuse, neoplasms, inherited bleeding diatheses, or acquired coagulopathies. Assessment of airway, breathing, and circulation precedes identification of bleeding source, pain control, and achieving hemostasis. Management options include topical vasoconstrictors, direct pressure, cautery, tranexamic acid, nasal tampons, Foley catheters, or surgical intervention. Specialty consultation may be pursued if interventions fail. Disposition is typically to home unless posterior epistaxis or significant comorbidities exist that warrant admission.
https://ift.tt/2PylCGw
The Diagnosis and Management of Facial Bone Fractures
Appropriate medical care for a patient with a facial fracture can not only optimize aesthetic outcomes but also prevent the potential morbidity and mortality of delayed treatment. In this article, we focus on the clinical presentations, physical examination findings, diagnostic imaging, consultations, and follow-up that patients with facial fractures need related to their emergency department management. Specifically, we address the nuances of evaluating frontal, orbital, nasal, maxillofacial, and mandibular fractures.
https://ift.tt/2QJRggC
Heteroatom‐Doped Carbon Materials for Hydrazine Oxidation

The development of heteroatom‐doped carbon electrocatalysts for the hydrazine oxidation reaction for direct hydrazine fuel cells and their general properties and structure‐related electrocatalytic activities are described with reference to the recent research progress and advancements. Perspectives on the different future research directions for these materials are also discussed.
Abstract
The key in designing efficient direct liquid fuel cells (DLFCs), which can offer some solutions to society's grand challenges associated with sustainability and energy future, currently lies in the development of cost‐effective electrocatalysts. Among the many types of fuel cells, direct hydrazine fuel cells (DHFCs) are of particular interest, especially due to their high theoretical cell voltages and clean emission. However, DHFCs currently use noble‐metal‐based electrocatalysts, and the scarcity and high cost of noble metals are hindering these fuel cells from finding large‐scale practical applications. In order to replace noble‐metal‐based electrocatalysts with sustainable ones and help DHFCs become widely usable, great efforts are being made to develop stable heteroatom (e.g., B, N, O, P and S)‐doped carbon electrocatalysts, the activities of which are comparable to, or better than, those of noble metals. Here, the recent research progress and the advancements made on the development of heteroatom‐doped carbon materials, their general properties, their electrocatalytic activities toward the HzOR, and their dopant‐ and structure‐related electrocatalytic properties for the HzOR are summarized. Perspectives on the different directions that the research endeavors in this field need to take in the future and the challenges associated with DHFCs are included.
https://ift.tt/2PzOrSE
Organic Photovoltaics with Multiple Donor–Acceptor Pairs

Utilizing multiple donor–acceptor pairs for organic solar cells (OSCs) is a very effective strategy for overcoming the limitations of conventional OSCs based on a single donor–acceptor pair. Recent cases of OSCs with multiple donor–acceptor pairs are not only summarized but their perspectives are also presented.
Abstract
Compared with conventional organic solar cells (OSCs) based on single donor–acceptor pairs, terpolymer‐ and ternary‐based OSCs featuring multiple donor–acceptor pairs are promising strategies for enhancing the performance while maintaining an easy and simple synthetic process. Using multiple donor–acceptor pairs in the active layer, the key photovoltaic parameters (i.e., short‐circuit current density, open‐circuit voltage, and fill factor) governing the OSC characteristics can be simultaneously or individually improved by positive changes in light‐harvesting ability, molecular energy levels, and blend morphology. Here, these three major contributions are discussed with the aim of offering in‐depth insights in combined terpolymers and ternary systems. Recent exemplary cases of OSCs with multiple donor–acceptor pairs are summarized and more advanced research and perspectives for further developments in this field are highlighted.
https://ift.tt/2QOT48d
Enzyme‐Instructed Supramolecular Self‐Assembly with Anticancer Activity

Enzyme‐instructed supramolecular self‐assembly (EISA) is a new strategy to combat cancer. Differentiated by certain thresholds of enzyme activities between normal and cancer cells, EISA can selectively assemble in cancer cells only. This multistep dynamic process exhibits anticancer activity via the induction of dysfunction of cell activities, targeted drug delivery, and so on.
Abstract
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death, which has continuously stimulated the development of numerous functional biomaterials with anticancer activities. Herein is reviewed one recent trend of biomaterials focusing on the advances in enzyme‐instructed supramolecular self‐assembly (EISA) with anticancer activity. EISA relies on enzymatic transformations to convert designed small‐molecular precursors into corresponding amphiphilic residues that can form assemblies in living systems. EISA has shown some advantages in controlling cell fate from three aspects. 1) Based on the abnormal activity of specific enzymes, EISA can differentiate cancer cells from normal cells. In contrast to the classical ligand–receptor recognition, the targeting capability of EISA relies on dynamic control of the self‐assembly process. 2) The interactions between EISA and cellular components directly disrupt cellular processes or pathways, resulting in cell death phenotypes. 3) EISA spatiotemporally controls the distribution of therapeutic agents, which boosts drug delivery efficiency. Therefore, with regard to the development of EISA, the aim is to provide a perspective on the future directions of research into EISA as anticancer theranostics.
https://ift.tt/2PvDB0d
Rollable, Stretchable, and Reconfigurable Graphene Hygroelectric Generators

Rollable, stretchable, and 3D space‐deformable graphene‐based hygroelectric generators are developed by a laser processing strategy, which exhibit excellent electricity‐generation ability without any significant performance loss despite being deformed arbitrarily, and are promising as power supply for applications in complicated conditions.
Abstract
Moisture‐triggered electricity generation has attracted much attention because of the effective utilization of the water‐molecule diffusion process widely existing in atmosphere. However, the monotonous and rigid structures of previously developed generators have heavily restricted their applications in complex and highly deformable working conditions. Herein, by a rational configuration design with a versatile laser processing strategy, graphene‐based hygroelectric generators (GHEGs) of sophisticated architectures with diversified functions such as rollable, stretchable, and even multidimensional transformation are achieved for the first time. More importantly, a wide range of 3D deformable generators that can automatically assemble and transform from planar geometries into spacial architectures are also successfully fabricated, including cubic boxes, pyramids, Miura‐ori, and footballs. These GHEGs demonstrate excellent electricity‐generation performance in curling and elongating states. The generated voltages are easily up to 1.5 V under humidity variation in atmosphere, powering a variety of commercial electronic components. These deformable GHEGs can be applied on complicated surfaces, human bodies, and many more beyond those demonstrated in this work.
https://ift.tt/2QNUoYR
Design for Highly Piezoelectric and Visible/Near‐Infrared Photoresponsive Perovskite Oxides

Perovskite oxides with high piezoelectricity and low bandgap are realized by an efficient strategy. For example, the Ni2+ mediated (1‐x)Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3‐xBa(Ti0.5Ni0.5)O3–δ with morphotropic phase boundary composition, shows enhanced piezoelectricity and exhibits three gap states with lowest sub‐bandgap of 0.9 eV that is responsible for visible/near‐infrared absorption. The designed ferroelectric semiconductor is very promising for multifunctional applications.
Abstract
Defect‐engineered perovskite oxides that exhibit ferroelectric and photovoltaic properties are promising multifunctional materials. Though introducing gap states by transition metal doping on the perovskite B‐site can obtain low bandgap (i.e., 1.1–3.8 eV), the electrically leaky perovskite oxides generally lose piezoelectricity mainly due to oxygen vacancies. Therefore, the development of highly piezoelectric ferroelectric semiconductor remains challenging. Here, inspired by point‐defect‐mediated large piezoelectricity in ferroelectrics especially at the morphotropic phase boundary (MPB) region, an efficient strategy is proposed by judiciously introducing the gap states at the MPB where defect‐induced local polar heterogeneities are thermodynamically coupled with the host polarization to simultaneously achieve high piezoelectricity and low bandgap. A concrete example, Ni2+‐mediated (1–x)Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3‐xBa(Ti0.5Ni0.5)O3–δ (x = 0.02–0.08) composition is presented, which can show excellent piezoelectricity and unprecedented visible/near‐infrared light absorption with a lowest ever bandgap ≈0.9 eV at room temperature. In particular, the MPB composition x = 0.05 shows the best ferroelectricity/piezoelectricity (d 33 = 151 pC N–1, Pr = 31.2 μC cm–2) and a largely enhanced photocurrent density approximately two orders of magnitude higher compared with classic ferroelectric (Pb,La)(Zr,Ti)O3. This research provides a new paradigm for designing highly piezoelectric and visible/near‐infrared photoresponsive perovskite oxides for solar energy conversion, near‐infrared detection, and other multifunctional applications.
https://ift.tt/2PzOm1i
Direct CVD Growth of Graphene on Traditional Glass: Methods and Mechanisms

A summary of the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) growth techniques of graphene on traditional glass as well as the growth mechanisms is provided. Direct thermal CVD growth, molten‐bed CVD growth, metal‐catalyst‐assisted growth, and plasma‐enhanced growth are covered. Emphasis is laid on the strategy of growth corresponding to the different natures of glass substrates.
Abstract
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on catalytic metal surfaces is considered to be the most effective way to obtain large‐area, high‐quality graphene films. For practical applications, a transfer process from metal catalysts to target substrates (e.g., poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET), glass, and SiO2/Si) is unavoidable and severely degrades the quality of graphene. In particular, the direct growth of graphene on glass can avoid the tedious transfer process and endow traditional glass with prominent electrical and thermal conductivities. Such a combination of graphene and glass creates a new type of glass, the so‐called "super graphene glass," which has attracted great interest from the viewpoints of both fundamental research and daily‐life applications. In the last few years, great progress has been achieved in pursuit of this goal. Here, these growth methods as well as the specific growth mechanisms of graphene on glass surfaces are summarized. The typical techniques developed include direct thermal CVD growth, molten‐bed CVD growth, metal‐catalyst‐assisted growth, and plasma‐enhanced growth. Emphasis is placed on the strategy of growth corresponding to the different natures of glass substrates. A comprehensive understanding of graphene growth on nonmetal glass substrates and the latest status of "super graphene glass" production are provided.
https://ift.tt/2QJQ250
The Absence and Importance of Operando Techniques for Metal‐Free Catalysts

Operando characterization techniques are nearly completely absent from the metal‐free‐catalyst literature. The reason for this absence and the importance of operando techniques, along with potential techniques, are discussed.
Abstract
Operando characterization techniques have played a crucial role in modern technological developments. In contrast to the experimental uncertainties introduced by ex situ techniques, the simultaneous measurement of desired sample characteristics and near‐realistic electrochemical testing provides a representative picture of the underlying physics. From Li‐ion batteries to metal‐based electrocatalysts, the insights offered by real‐time characterization data have enabled more efficient research programs. As an emerging class of catalyst, much of the mechanistic understanding of metal‐free electrocatalysts continues to be elusive in comparison to their metal‐based counterparts. However, there is a clear absence of operando characterization performed on metal‐free catalysts. Through the proper execution of operando techniques, it can be expected that metal‐free catalysts can achieve exceptional technological progress. Here, the motivation of using operando characterization techniques for metal‐free carbon‐based catalyst system is considered, followed by a discussion of the possibilities, difficulties and benefits of their applications.
https://ift.tt/2Py4Mat
{-}{-}{-}{-}Immunotherapy for Glioblastoma: Adoptive T-cell Strategies
Glioblastoma (GBM) is a devastating disease with an extremely poor prognosis. Immune therapy via adoptive cell transfer (ACT), especially with T cells engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), represents a particularly promising approach. Despite the recent success of CAR T cells for blood cancers, the question remains whether this powerful anti-cancer therapy will ultimately work for brain tumors, and if the primary immunologic challenges in this disease-which include antigenic heterogeneity, immune suppression and T-cell exhaustion-can be adequately addressed. Here, we contextualize these concepts by reviewing recent developments in ACT for GBM, with a special focus on pioneering clinical trials of CAR T-cell therapy.
https://ift.tt/2qS4Cfo
Inhibition of LEF1-mediated DCLK1 by Niclosamide Attenuates Colorectal Cancer Stemness
Purpose: Niclosamide, an FDA-approved anthelmintic drug, has been characterized as a potent Wnt inhibitor that can suppress tumor growth and cancer stem-like cell (CSC) populations. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. The current study aimed to examine how Wnt inhibition by niclosamide preferentially targets CSCs. Experimental Design: The mechanistic role of niclosamide in CSC inhibition was examined in public databases, human colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, CRC xenografts, and azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium (AOM/DSS)-induced CRC model. Results: Niclosamide suppresses CSC populations and their self-renewal activities in CRC cells, and this CSC-targeting effect leads to irreversible disruption of tumor-initiating potential in vivo. Mechanistically, niclosamide downregulates multiple signaling components of the Wnt pathway, specifically lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 (LEF1) expression, which is critical for regulating stemness. Subsequently, we identified that the doublecortin-like kinase1 (DCLK1)-B is a target of LEF1 and upregulates cancer stemness in CRC cells. We first documented that niclosamide blocks the transcription of DCLK1-B by interrupting the binding of LEF1 to DCLK1-B promoter. DCLK1-B depletion impairs cancer stemness resulting in reduced survival potential and increased apoptosis, thus sensitizing CRC to chemoradiation. Conclusions: Disruption of the LEF1/DCLK1-B axis by niclosamide eradicates cancer stemness and elicits therapeutic effects on CRC initiation, progression, and resistance. These findings provide a preclinical rationale to broaden the clinical evaluation of niclosamide for the treatment of CRC.
https://ift.tt/2FshKlL
Neutrophil extracellular traps induced by IL-8 promote diffuse large B cell lymphoma progression via the TLR9 signaling
Purpose: Over 30% of patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) experience treatment failure after first-line therapy. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), a pathogen-trapping structure in tumor microenvironment, can promote the transition of autoimmunity to lymphomagenesis. Here, we investigate whether NETs play a novel role in DLBCL progression and its underlying mechanism. Experimental Design: NETs in DLBCL tumor samples and plasma were detected by immunofluorescence and ELISA, respectively. The correlation between NETs and clinical features were analyzed. The effects of NETs on cellular proliferation and migration and mechanisms were explored. And the mechanism of NET formation was also studied by a series of in vitro and in vivo assays. Results: Higher levels of NETs in plasma and tumor tissues were associated with dismal outcome in DLBCL patients. Further, we identified NETs increased cell proliferation and migration in vitro and tumor growth and lymph nodal dissemination in vivo. Mechanistically, DLBCL-derived IL-8 interacted with its receptor (CXCR2) on neutrophils, resulting in the formation of NETs via Src, p38 and ERK signaling. Newly formed NETs directly upregulated the Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) pathways in DLBCL and subsequently activated NF-B, STAT3 and p38 pathways to promote tumor progression. More importantly, disruption of NETs, blocking IL-8-CXCR2 axis or inhibiting TLR9 could retard tumor progression in preclinical models. Conclusions: Our data reveal a tumor-NETs aggressive interaction in DLBCL, and indicate that NETs is a useful prognostic biomarker and targeting this novel crosstalk represents a new therapeutic opportunity in this challenging disease.
https://ift.tt/2qOCABw
Predicting Treatment Response Based on RNA Expression in Large Datasets
PD-L1 expression levels derived from >16,000 samples guided the selection of tumor types likely to benefit from pembrolizuamb monotherapy in clinical trials. While not fail-proof, FDA approvals for most of the prioritized indications speak to the power of RNA expression profiling and the value of large genomic datasets.
https://ift.tt/2FoNt75
Only Human
I feel like a murderer she saidI knew what she meantIt was never intentionalOr expectedYou knew what you were getting intoYou took The OathYou studied for itMemorized itSimulated itBut nothing prepares you for itThe first mistakeThe first Oh My GodThe first I-wish-I-could-do-that-overI'd-do-it-a-thousand-different-waysOr maybe just one.And yet here you areWishing you had had just maybe an extra few minutes to think, to breathe, to prepare for That PatientBut you didn'tAnd you did the best you could in the momentOr you try to convince yourself you didHow did I miss it?Would my partner have missed it?Has anyone done this beforeShould I ask?Who do I even askDoes anyone else suffer this way?The lonely and the isolatedThe one here to saveneeds savingSave me from my thoughts, my fearsMyselfI did this to myselfAnd to HimWho else can possibly understandExcept my ownI just wish I knew who they were.
https://ift.tt/2zdZgzC
Man With Abdominal Pain and Bilious Emesis
A 62-year-old man with diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and atrial fibrillation presented to our emergency department with sudden-onset abdominal pain and bilious emesis. Initial vital signs showed a blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg, pulse rate of 135 beats/min, and tympanic membrane temperature of 36.8°C (98.2°F). Physical examination was notable for a distended abdomen with rebound tenderness and hypoactive bowel sounds. Initial laboratory testing result was notable for leukocytosis. Noncontrast enhanced abdominal computed tomography (CT) showed extensive gas in the mesenteric and hepatic portal venous system, and small bowel dilatation with pneumatosis (Figures 1 to 4).
https://ift.tt/2OP8Y0j
Man With Left-Sided Neck Pain
A 52-year-old man with a history of controlled hypertension presented to the emergency department (ED) with a 9-day history of nontraumatic left-sided neck pain. The patient had visited the ED on 3 previous occasions, where he received a diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain and was treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories, without relief.
https://ift.tt/2zd1xva
In reply:
In the article titled "Potentially Avoidable Emergency Department Use: When Policy Expects Patients to Be Doctors,"1 we discussed the challenges of appropriately treating patients with acute care needs and the concerns with restricting access related to "potentially avoidable" emergency department (ED) use. We first described the current health policy context and then highlighted a promising strategy from a collaboration between payers and providers for bariatric surgery patients.
https://ift.tt/2zdoAWL
Elderly Woman With Abnormal ECG
A 76-year-old woman with hypertension (treated with amlodipine) and dyslipidemia was sent to the emergency department after an abnormal ECG result was obtained during a routine visit (Figure 1). She reported only a mild episode of resting nonanginal chest pain, lasting 10 minutes and occurring 1 month earlier. An ECG result obtained 6 months earlier was unremarkable (Figure 2). The patient was asymptomatic; vital signs and physical examination result were normal. Her troponin I level was 0.038 ng/mL (normal values <0.046 ng/mL).
https://ift.tt/2OKIpcF
Elderly Woman With Abdominal Pain
A 91-year-old woman presented to our emergency department with abdominal pain for 3 days. Her vital signs were normal and a physical examination showed localized tenderness in the epigastrium. Laboratory tests revealed leukocytosis and elevated liver function test results. After she complained of right lower quadrant abdominal pain, right lower quadrant tenderness and a positive psoas sign were noted. A surgeon was consulted because of the impression of acute appendicitis, and intravenous contrast–enhanced computed tomography (CT) of her abdomen was performed.
https://ift.tt/2zfVjur
Elderly Female With Syncope
A 77-year-old woman with a history of chronic kidney disease presented to the emergency department (ED) by ambulance. The patient was found on the floor of her bedroom, reporting generalized weakness and numerous syncopal episodes. She reported dyspnea but denied chest pain. In the ED, she was alert and oriented. The cardiac monitor demonstrated intermittent bradycardia with frequent ectopy. A 12-lead ECG was obtained (Figure 1).
https://ift.tt/2OIK5nb
New Emergency Nurse Practitioner Certification Rolled Out
Nurse practitioners (NPs) have worked alongside emergency physicians for decades, but only in the past year has the profession gained a specialty certification. Now, by passing the Emergency Nurse Practitioner (ENP) Certification examination, NPs may add ENP-C to their list of credentials.
https://ift.tt/2zcQthk
Outpatient Pulmonary Embolism Management: If You Walk Into the Emergency Department With a Pulmonary Embolism, Maybe You Should Also Walk Out
Q1. Vinson et al1 performed this retrospective cohort study examining the outpatient management of patients with acute pulmonary embolism at 21 community emergency departments (EDs) in Northern California between January 2013 and April 2015. The study found that 7.5% of patients were discharged.
https://ift.tt/2ONI7BL
Research in Emergency Medicine: Building the Investigator Pipeline
SEE RELATED ARTICLE, P. 679.
https://ift.tt/2OOCmUs
Annals Q&A With Dr. Stephen Bergman
Forty years ago, Stephen Bergman, MD, DPhil, took a pen name, Samuel Shem, and published the most influential novel about the American hospital establishment ever written, The House of God. After his intern year at Beth Israel Hospital (now Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center) in Bosto Shem, as he still prefers to be called by his colleagues, went on to practice psychiatry before leaving medicine entirely in the 1990s to focus on what had always been his first love: writing. The author of several novels and a play cowritten with his wife, Janet Surrey, about the founding of Alcoholics Anonymous, Bill W.
https://ift.tt/2zfVjdV
Global Research Highlights
Editor's note: Annals has partnered with a small group of selected journals of international emergency medicine societies to share from each a highlighted research study, as selected monthly by their editors. Our goals are to increase awareness of our readership to research developments in the international emergency medicine literature, promote collaboration among the selected international emergency medicine journals, and support the improvement of emergency medicine world-wide, as described in the WAME statement at https://ift.tt/2dmKsCb.
https://ift.tt/2ONnOV2
Calendar
▮ 39th Annual Current Concepts in Emergency Care 2018. December 2–8, 2018. Maui, HI. Contact: Amy Losee. Email: amy@emergenciesinmedicine.com. Url: https://ift.tt/2zd1wY8. (28.50)
https://ift.tt/2OQgOqG
Classified
FLORIDA, Port Charlotte: Stable, 22 year old, progressive independent group seeking residency trained, board certified emergency physicians for expansion to second facility. 27k and 22k volume EDs. Full specialty backup. Excellent compensation based on productivity with full time income potential exceeding 350k. Flexible scheduling. Documentation by EMR. Malpractice, Health Insurance, Dental provided. Located on Charlotte Harbor with saltwater access to the Gulf. Short drive to Tampa, Sarasota, Fort Myers, Naples.
https://ift.tt/2ONntC7
Woman With Foreign Body on Her Tongue
A 38-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a foreign body on her tongue. After intake of sushi including raw squid for lunch, she had discomfort, with a sensation of something sticking to her tongue. Ten hours after lunch, she coughed up a small piece of squid and noticed some white threadlike material stuck to her tongue (Figures 1 and 2). Although she tried to remove it, she could not.
https://ift.tt/2OSKQu4
Woman With Neck Pain
A 55-year-old woman presented with 24 hours of neck pain, odynophagia, and painful foreign body sensation that began while she ate a sandwich. Vital signs were normal. Physical examination showed a nontoxic woman, muffled voice, clear oropharynx, and pain with neck extension. WBC count was 18.8×103/μL. Neck computed tomography (CT) was obtained (Figure 1). Clindamycin and dexamethasone were given intravenously, and an otolaryngologist performed direct laryngoscopy in the operating room (Figure 2).
https://ift.tt/2zbJDbV
Use of Blood Biomarkers in the Assessment of Sports-Related Concussion—A Systematic Review in the Context of Their Biological Significance
 Objectives: To critically review current knowledge on the positive and negative predictive value of blood biomarkers for concussion; to illustrate the clinical and biological contexts that help evaluate the use of these markers in sport-related traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). Methods: This systematic review was performed in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. We reviewed the measurement, clinical utility, endpoint, and biological significance of blood biomarkers in concussion. Results: A total of 4352 publications were identified. Twenty-six articles relating to blood biomarkers were included in the review. Four common blood biomarkers, namely S100B, tau, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), were examined. Overall, the studies showed S100B measurement and use, either acutely or at several time points, can distinguish injured from noninjured patients with an uncertain degree of utility in predicting mortality. At present, S100B has largely become an acceptable biomarker of TBI; however, studies have begun to highlight the need to incorporate clinical symptoms instead of S100B concentration in isolation on the basis of inconsistent results and lack of specificity across published studies. Further research is needed to evaluate and validate the use of tau, NSE, and GFAP as a diagnostic aid in the management of concussion and TBI. Conclusions: At present, blood biomarkers have only a limited role in the evaluation and management of concussion. Although several biomarkers of brain injury have been identified, continued research is required. S100B holds promise as the most clinically useful diagnostic biomarker. Blood biomarkers, in combination with other clinical data, such as head computed tomography, would maximize the diagnostic accuracy. The methodological limitations evident in blood biomarker research results in the need for the clinical utility of blood biomarker use in concussion to be further explored.
Objectives: To critically review current knowledge on the positive and negative predictive value of blood biomarkers for concussion; to illustrate the clinical and biological contexts that help evaluate the use of these markers in sport-related traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). Methods: This systematic review was performed in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. We reviewed the measurement, clinical utility, endpoint, and biological significance of blood biomarkers in concussion. Results: A total of 4352 publications were identified. Twenty-six articles relating to blood biomarkers were included in the review. Four common blood biomarkers, namely S100B, tau, neuron-specific enolase (NSE), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), were examined. Overall, the studies showed S100B measurement and use, either acutely or at several time points, can distinguish injured from noninjured patients with an uncertain degree of utility in predicting mortality. At present, S100B has largely become an acceptable biomarker of TBI; however, studies have begun to highlight the need to incorporate clinical symptoms instead of S100B concentration in isolation on the basis of inconsistent results and lack of specificity across published studies. Further research is needed to evaluate and validate the use of tau, NSE, and GFAP as a diagnostic aid in the management of concussion and TBI. Conclusions: At present, blood biomarkers have only a limited role in the evaluation and management of concussion. Although several biomarkers of brain injury have been identified, continued research is required. S100B holds promise as the most clinically useful diagnostic biomarker. Blood biomarkers, in combination with other clinical data, such as head computed tomography, would maximize the diagnostic accuracy. The methodological limitations evident in blood biomarker research results in the need for the clinical utility of blood biomarker use in concussion to be further explored.https://ift.tt/2QQMqhx
Effects of Intravenous Cold Saline on Hyperthermic Athletes Representative of Large Football Players and Small Endurance Runners
 Objective: To evaluate the cooling effects of intravenous (IV) cold normal (0.9%) saline on hyperthermic athletes. Design: Randomized crossover study design. Setting: Controlled research laboratory. Participants: Twelve male participants who were representative of a collegiate cross-country (6) and American football (6) population. Interventions: Participants underwent body composition analysis using a BodPod. They were placed in an environmentally controlled chamber and brought to a Tc of 39.5°C with dynamic exercise. When temperatures were reached, they were treated with either 2 L of cold saline (CS) (4°C) or intravenous room temperature (22°C) saline (RS) over a ∼30-minute period. Tre was measured with a rectal temperature probe every minute during the treatment period. Main Outcome Measures: Total ΔTre (ending Tre − starting Tre) and cooling rate (total change in Tre/time) were measured for each condition, and body composition variables calculated included body surface area (BSA), BSA-to-mass ratio (BSA/mass), lean body mass, and body fat percentage (%BF) (P
Objective: To evaluate the cooling effects of intravenous (IV) cold normal (0.9%) saline on hyperthermic athletes. Design: Randomized crossover study design. Setting: Controlled research laboratory. Participants: Twelve male participants who were representative of a collegiate cross-country (6) and American football (6) population. Interventions: Participants underwent body composition analysis using a BodPod. They were placed in an environmentally controlled chamber and brought to a Tc of 39.5°C with dynamic exercise. When temperatures were reached, they were treated with either 2 L of cold saline (CS) (4°C) or intravenous room temperature (22°C) saline (RS) over a ∼30-minute period. Tre was measured with a rectal temperature probe every minute during the treatment period. Main Outcome Measures: Total ΔTre (ending Tre − starting Tre) and cooling rate (total change in Tre/time) were measured for each condition, and body composition variables calculated included body surface area (BSA), BSA-to-mass ratio (BSA/mass), lean body mass, and body fat percentage (%BF) (Phttps://ift.tt/2PvygpH
Effects of 12-Week Resistance Exercise on Electroencephalogram Patterns and Cognitive Function in the Elderly With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial
 Objective: To investigate the effects of a 12-week resistance exercise program with an elastic band on electroencephalogram (EEG) patterns and cognitive function in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Design: Randomized controlled trial. Setting: Community center. Participants: Twenty-two subjects with MCI and 25 healthy volunteer subjects were randomly assigned to 1 of 4 groups: subjects with MCI who undertook the exercise program (MCI-EX; n = 10), an MCI control group (MCI-Con; n = 12), a healthy volunteer exercise group (NG-EX; n = 12), and a healthy volunteer control group (NG-Con; n = 13). Intervention: The exercise group engaged in a 15-repetition maximum (15RM; 65% of 1RM) resistance exercise program for 12 weeks. Main Outcome Measures: Electroencephalograms, neuropsychological tests, and Senior Fitness Test. Results: The 12-week 15RM (65% of 1RM) resistance exercise program significantly improved variables related to the physical fitness of the elderly subjects. Furthermore, for the EEG test, the MCI and NG groups showed significant differences at baseline in relative beta waves on electrodes Fp1 (P
Objective: To investigate the effects of a 12-week resistance exercise program with an elastic band on electroencephalogram (EEG) patterns and cognitive function in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Design: Randomized controlled trial. Setting: Community center. Participants: Twenty-two subjects with MCI and 25 healthy volunteer subjects were randomly assigned to 1 of 4 groups: subjects with MCI who undertook the exercise program (MCI-EX; n = 10), an MCI control group (MCI-Con; n = 12), a healthy volunteer exercise group (NG-EX; n = 12), and a healthy volunteer control group (NG-Con; n = 13). Intervention: The exercise group engaged in a 15-repetition maximum (15RM; 65% of 1RM) resistance exercise program for 12 weeks. Main Outcome Measures: Electroencephalograms, neuropsychological tests, and Senior Fitness Test. Results: The 12-week 15RM (65% of 1RM) resistance exercise program significantly improved variables related to the physical fitness of the elderly subjects. Furthermore, for the EEG test, the MCI and NG groups showed significant differences at baseline in relative beta waves on electrodes Fp1 (Phttps://ift.tt/2PwUJmn
Reactive Osteochondromatous Lesion of the Femoral Neck in a Highly Active Preadolescent Patient: Is This the Pathogenesis of a Cam Deformity?
 Abstract: Here, we present a rare case of a preadolescent boy with a prominent bony bump on the femoral neck. The main histological feature was concordant with a reactive osteochondromatous lesion possibly induced by repetitive microtrauma, probably because of overtraining as a soccer goalkeeper. The nature of this pathological change is consistent with the growth of a cam deformity. Especially in the preadolescent age group, we should note that repetitive use of the same joint kinematics may induce a prominent cam deformity.
Abstract: Here, we present a rare case of a preadolescent boy with a prominent bony bump on the femoral neck. The main histological feature was concordant with a reactive osteochondromatous lesion possibly induced by repetitive microtrauma, probably because of overtraining as a soccer goalkeeper. The nature of this pathological change is consistent with the growth of a cam deformity. Especially in the preadolescent age group, we should note that repetitive use of the same joint kinematics may induce a prominent cam deformity.https://ift.tt/2QPRiDC
Postexercise Hypotension as a Predictor for Long-Term Training-Induced Blood Pressure Reduction: A Large-Scale Randomized Controlled Trial
 Objective: To investigate the correlation between acute exercise effects and chronic training effects on blood pressure (BP). Design: Randomized, controlled training study focusing on the optimization of preventive effects of physical training. Setting: The study was performed in a university department. Participants: One hundred twenty-seven healthy, untrained subjects. Intervention: Subjects were divided into 4 groups: interval endurance training (IET) (n = 26, 4 × 4 min at 95% maximal heart rate), continuous endurance training (CET) (n = 23, 45 minutes at 60% heart rate reserve), strength endurance training (SET) (n = 40, 8 machine-based exercises, each 2 x 15 repetitions at the 20 repetition maximum), and control (CON) (n = 38). In the 3 training groups, subjects trained 3 times a week for 6 months, the CON group was asked to retain their sedentary lifestyle. Main Outcome Measures: The acute exercise effect on BP was defined as the change of BP after an exhaustive stage test, compared with baseline. The chronic training effect on BP was determined as the change of resting BP after the 6-month training period. Results: For CET, a significant correlation between acute and chronic effects on systolic (r = 0.66, P = 0.001) and diastolic (r = 0.66, P = 0.001) BP was observed. For SET, a significant correlation (r = 0.45, P = 0.007) was found only for diastolic BP. No significant correlations were found for IET. Conclusions: It can be assumed that postexercise hypotension is an easy-to-use predictor for the efficacy of CET to reduce BP, and may be a valuable tool for physicians to individualize prescribed training schedules for patients to reduce cardiovascular risk. Trial Registration: www.clinicaltrials.gov; ID: NCT01263522.
Objective: To investigate the correlation between acute exercise effects and chronic training effects on blood pressure (BP). Design: Randomized, controlled training study focusing on the optimization of preventive effects of physical training. Setting: The study was performed in a university department. Participants: One hundred twenty-seven healthy, untrained subjects. Intervention: Subjects were divided into 4 groups: interval endurance training (IET) (n = 26, 4 × 4 min at 95% maximal heart rate), continuous endurance training (CET) (n = 23, 45 minutes at 60% heart rate reserve), strength endurance training (SET) (n = 40, 8 machine-based exercises, each 2 x 15 repetitions at the 20 repetition maximum), and control (CON) (n = 38). In the 3 training groups, subjects trained 3 times a week for 6 months, the CON group was asked to retain their sedentary lifestyle. Main Outcome Measures: The acute exercise effect on BP was defined as the change of BP after an exhaustive stage test, compared with baseline. The chronic training effect on BP was determined as the change of resting BP after the 6-month training period. Results: For CET, a significant correlation between acute and chronic effects on systolic (r = 0.66, P = 0.001) and diastolic (r = 0.66, P = 0.001) BP was observed. For SET, a significant correlation (r = 0.45, P = 0.007) was found only for diastolic BP. No significant correlations were found for IET. Conclusions: It can be assumed that postexercise hypotension is an easy-to-use predictor for the efficacy of CET to reduce BP, and may be a valuable tool for physicians to individualize prescribed training schedules for patients to reduce cardiovascular risk. Trial Registration: www.clinicaltrials.gov; ID: NCT01263522.https://ift.tt/2PCJjgY
TRest as a New Diagnostic Variable for Chronic Exertional Compartment Syndrome of the Forearm: A Prospective Cohort Analysis of 124 Athletes
 Objectives: To measure the accuracy of currently used intracompartmental pressure (ICP) diagnostic variables for forearm chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) and a new ICP diagnostic variable, TRest, the recovery time between the maximum ICP and return to resting pressure. Design: Retrospective cohort. Level evidence IV. Setting: University-affiliated tertiary hospital. Participants: Patients with suspected forearm CECS, 1990 to 2014. Interventions: All patients underwent physical examination and exertional stress test, preceded and followed by measuring ICP in all suspicious CECS. Surgery was proposed when indicated. Minimum follow-up was 18 months. Final diagnosis was established at the final follow-up. Main Outcome Measures: Intracompartmental pressure measurements: PRest (baseline/pre-exercise pressure), P1 min (pressure 1 minute after exercise), P5 min (pressure 5 minutes after exercise), and TRest. Patients rated their pain and completed Quick-DASH in all follow-ups. Patients ultimately were classified into 4 groups (true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives) for each ICP measurement relative to the final diagnosis. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated. Results: A total of 124 male athletes were diagnosed with CECS, 27 bilateral. Accuracy with standard ICP diagnostic variables was lower (sensitivity 73.5%, specificity 84.2%, positive predictive value 97%, and negative predictive value 31.4%) than with TRest (SN 100%, SP 94.7%, PPV 99.3%, and NPV 100%); 23% of patients would have been missed following the standard ICP diagnostic criteria. Conclusions: Diagnostic thresholds for current standard ICP measurements should be lowered. TRest, a new measure, might be more accurate.
Objectives: To measure the accuracy of currently used intracompartmental pressure (ICP) diagnostic variables for forearm chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) and a new ICP diagnostic variable, TRest, the recovery time between the maximum ICP and return to resting pressure. Design: Retrospective cohort. Level evidence IV. Setting: University-affiliated tertiary hospital. Participants: Patients with suspected forearm CECS, 1990 to 2014. Interventions: All patients underwent physical examination and exertional stress test, preceded and followed by measuring ICP in all suspicious CECS. Surgery was proposed when indicated. Minimum follow-up was 18 months. Final diagnosis was established at the final follow-up. Main Outcome Measures: Intracompartmental pressure measurements: PRest (baseline/pre-exercise pressure), P1 min (pressure 1 minute after exercise), P5 min (pressure 5 minutes after exercise), and TRest. Patients rated their pain and completed Quick-DASH in all follow-ups. Patients ultimately were classified into 4 groups (true positives, true negatives, false positives, and false negatives) for each ICP measurement relative to the final diagnosis. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated. Results: A total of 124 male athletes were diagnosed with CECS, 27 bilateral. Accuracy with standard ICP diagnostic variables was lower (sensitivity 73.5%, specificity 84.2%, positive predictive value 97%, and negative predictive value 31.4%) than with TRest (SN 100%, SP 94.7%, PPV 99.3%, and NPV 100%); 23% of patients would have been missed following the standard ICP diagnostic criteria. Conclusions: Diagnostic thresholds for current standard ICP measurements should be lowered. TRest, a new measure, might be more accurate.https://ift.tt/2PAceBY
Strengths, Limitations, and Geographical Discrepancies in the Eligibility Criteria for Sport Participation in Young Patients With Congenital Heart Disease
 Objective: Benefits of physical activity has been shown in children with congenital heart disease (CHD). In several forms of CHD, the risk of sudden death remains a major concern both for parents and clinicians, who in turn will have to consider the risk–benefit ratio of sport participation versus restriction. Data source: A literature search was performed within the National Library of Medicine using the keywords: Sport, CHD, and Eligibility. The search was further refined by adding the keywords: Children, Adult, and Criteria. Main Results: Fifteen published studies evaluating sport eligibility criteria in CHD were included. Seven documents from various scientific societies have been published in the past decade but which of them should be adopted remains unclear. Our research highlighted accuracy and consistency of the latest documents; however, differences have emerged between the US and European recommendations. Eligibility criteria were consistent between countries for simple congenital heart defects, whereas there are discrepancies for borderline conditions including moderate valvular lesions and mild or moderate residual defects after CHD repair. Furthermore, some of the more severe defects were not evaluated. Multiple recommendations have been made for the same CHD, and cut-off values used to define disease severity have varied. Published eligibility criteria have mainly focused on competitive sports. Little attention was paid to recreational activities, and the psychosocial consequences of activity restriction were seldom evaluated. Conclusions: Comprehensive consensus recommendations for sport eligibility evaluating all CHD types and stages of repair are needed. These should include competitive and recreational activities, use standardized classifications to grade disease severity, and address the consequences of restriction.
Objective: Benefits of physical activity has been shown in children with congenital heart disease (CHD). In several forms of CHD, the risk of sudden death remains a major concern both for parents and clinicians, who in turn will have to consider the risk–benefit ratio of sport participation versus restriction. Data source: A literature search was performed within the National Library of Medicine using the keywords: Sport, CHD, and Eligibility. The search was further refined by adding the keywords: Children, Adult, and Criteria. Main Results: Fifteen published studies evaluating sport eligibility criteria in CHD were included. Seven documents from various scientific societies have been published in the past decade but which of them should be adopted remains unclear. Our research highlighted accuracy and consistency of the latest documents; however, differences have emerged between the US and European recommendations. Eligibility criteria were consistent between countries for simple congenital heart defects, whereas there are discrepancies for borderline conditions including moderate valvular lesions and mild or moderate residual defects after CHD repair. Furthermore, some of the more severe defects were not evaluated. Multiple recommendations have been made for the same CHD, and cut-off values used to define disease severity have varied. Published eligibility criteria have mainly focused on competitive sports. Little attention was paid to recreational activities, and the psychosocial consequences of activity restriction were seldom evaluated. Conclusions: Comprehensive consensus recommendations for sport eligibility evaluating all CHD types and stages of repair are needed. These should include competitive and recreational activities, use standardized classifications to grade disease severity, and address the consequences of restriction.https://ift.tt/2QPoewj
Shoulder Injuries in Canoeing and Kayaking
 Objective: We report the largest case series of shoulder injuries among paddlers so far to establish common mechanisms and patterns of injury. We also discuss how these injuries were managed and report the proportion of paddlers that return to paddlesport. Design: Case series. Setting: Upper Limb Unit, Wrightington Hospital, United Kingdom. Manchester Arm Clinic, United Kingdom. Patients: Fifty-seven shoulder injuries to professional and recreational paddlers were reviewed at a mean follow-up time of 55 months from the first consultation. The patient cohort had a mean age of 36 years and consisted of 56% males. Assessment of Risk Factors: Sex, mechanism of injury, acute/nonacute injury, and level of sport participation. Main Outcome Measures: Patient data were analyzed with regards to Constant score, QuickDASH score, and VAS satisfaction score before and after treatment. Results: The most common mechanism of injury was a capsize which accounted for 15 (26%) injuries. Ten injuries caused by a capsize were labral tears all of which needed surgery. A significant improvement in patient outcome scores was noted. Patients were able to return to a high level of paddling such as 3 slalom paddlers who returned to international competition; one of whom had bilateral surgery. Conclusions: Paddlers most commonly injure their shoulder when preventing a capsize, during a capsize or while rolling. The paddles strokes performed at these times often require paddlers to place their shoulder in a dangerous abducted and externally rotated position. We believe this is one of the commonest causes of serious shoulder injuries to paddlers.
Objective: We report the largest case series of shoulder injuries among paddlers so far to establish common mechanisms and patterns of injury. We also discuss how these injuries were managed and report the proportion of paddlers that return to paddlesport. Design: Case series. Setting: Upper Limb Unit, Wrightington Hospital, United Kingdom. Manchester Arm Clinic, United Kingdom. Patients: Fifty-seven shoulder injuries to professional and recreational paddlers were reviewed at a mean follow-up time of 55 months from the first consultation. The patient cohort had a mean age of 36 years and consisted of 56% males. Assessment of Risk Factors: Sex, mechanism of injury, acute/nonacute injury, and level of sport participation. Main Outcome Measures: Patient data were analyzed with regards to Constant score, QuickDASH score, and VAS satisfaction score before and after treatment. Results: The most common mechanism of injury was a capsize which accounted for 15 (26%) injuries. Ten injuries caused by a capsize were labral tears all of which needed surgery. A significant improvement in patient outcome scores was noted. Patients were able to return to a high level of paddling such as 3 slalom paddlers who returned to international competition; one of whom had bilateral surgery. Conclusions: Paddlers most commonly injure their shoulder when preventing a capsize, during a capsize or while rolling. The paddles strokes performed at these times often require paddlers to place their shoulder in a dangerous abducted and externally rotated position. We believe this is one of the commonest causes of serious shoulder injuries to paddlers.https://ift.tt/2Pxodk2
Syncope Episodes and Blood Flow Restriction Training
 Abstract: The combination of low-load resistance training [or more recently, neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)] with a moderate local blood flow restriction (BFR) is becoming a widespread training and rehabilitation method. Scientific data indicate the overall safety of BFR, at least in healthy young people. However, it has been associated with side effects, usually minor, and further research is warranted regarding the safety and efficacy of this technique, especially in clinical populations. We found 3 syncope/presyncopal episodes among 21 healthy people (9 men), all occurring in men and during familiarization sessions (in which BFR was applied alone) but not thereafter (BFR sessions combined with NMES): 1 subject experienced a brief syncope and 2 other subjects exhibited presyncopal symptoms (sweating, lightheadedness, and pallor). Our cases are evidence that cardiovascular complications may emerge during BFR. Caution is thus needed in the application of BFR, and gentle familiarization with this training modality is also recommended.
Abstract: The combination of low-load resistance training [or more recently, neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)] with a moderate local blood flow restriction (BFR) is becoming a widespread training and rehabilitation method. Scientific data indicate the overall safety of BFR, at least in healthy young people. However, it has been associated with side effects, usually minor, and further research is warranted regarding the safety and efficacy of this technique, especially in clinical populations. We found 3 syncope/presyncopal episodes among 21 healthy people (9 men), all occurring in men and during familiarization sessions (in which BFR was applied alone) but not thereafter (BFR sessions combined with NMES): 1 subject experienced a brief syncope and 2 other subjects exhibited presyncopal symptoms (sweating, lightheadedness, and pallor). Our cases are evidence that cardiovascular complications may emerge during BFR. Caution is thus needed in the application of BFR, and gentle familiarization with this training modality is also recommended.https://ift.tt/2QKIW09
Preparticipation Sports Physicals: A Comparison of Single Provider and Station-Based Models
 Background: Preparticipation physical examinations (PPEs) are required for children and adolescents before sports participation to identify at-risk athletes. These evaluations can be completed in a traditional office-based setting or in a station-based format. It is unclear if one format is superior to the other in identifying at-risk athletes. Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of children and adolescents between the ages 10 and 18 years who received their PPE in our office or in a station-based setting in a local high school between the years 2009 and 2015. Results: We reviewed 2934 PPEs total, 1136 in the office-based format and 1798 in the station-based setting. A similar proportion of athletes were excluded or required further evaluation before participation in the office compared with the station-based setting (4.84% vs 5.67%). No statistically significant associations were seen between site of PPE or athlete sex and rate of clearance. There was, however, a statistically significant association between PPE site and reason for exclusion (P = 0.0456) with higher rates of exclusion for vision-related issues in the station-based setting and higher rates of exclusion for musculoskeletal or cardiopulmonary reasons in the office-based setting. Conclusion: When conducted by the same examiners, the office-based and team-based PPE excluded or referred equal number of athletes, although the reason for further evaluation does differ based on setting.
Background: Preparticipation physical examinations (PPEs) are required for children and adolescents before sports participation to identify at-risk athletes. These evaluations can be completed in a traditional office-based setting or in a station-based format. It is unclear if one format is superior to the other in identifying at-risk athletes. Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of children and adolescents between the ages 10 and 18 years who received their PPE in our office or in a station-based setting in a local high school between the years 2009 and 2015. Results: We reviewed 2934 PPEs total, 1136 in the office-based format and 1798 in the station-based setting. A similar proportion of athletes were excluded or required further evaluation before participation in the office compared with the station-based setting (4.84% vs 5.67%). No statistically significant associations were seen between site of PPE or athlete sex and rate of clearance. There was, however, a statistically significant association between PPE site and reason for exclusion (P = 0.0456) with higher rates of exclusion for vision-related issues in the station-based setting and higher rates of exclusion for musculoskeletal or cardiopulmonary reasons in the office-based setting. Conclusion: When conducted by the same examiners, the office-based and team-based PPE excluded or referred equal number of athletes, although the reason for further evaluation does differ based on setting.https://ift.tt/2Pxo4x0
Decreased Average Power of the Hip External Muscles as a Predictive Parameter for Lower Extremity Injury in Women: A Prospective Study
 Objective: To prospectively identify hip strength associated risk factors contributing to the development of lower extremity (LE) injury. Design: Data were prospectively collected on healthy female physical education students. Setting: This study was conducted in the institution of the University of Ghent. Participants: Eighty-nine female physical education students aged 19.53 ± 1.07 years. Assessment of Risk Factors: Testing included isokinetic hip strength measurements of abductors, adductors, internal rotators, and external rotators (ERs). Main Outcome Measures: Follow-up of the participants was assessed using a weekly online questionnaire and a 3-month retrospective control questionnaire. Lower extremity injury was diagnosed by an experienced medical doctor. Cox regression was used to identify the potential risk factors for the development of an LE injury. Results: Thirty-four participants were diagnosed with an LE injury during follow-up. This study identified that decreased average power (AP) (P = 0.031) on concentric ER strength was found to be a significant risk factor for LE injury. No other hip strength parameters were found to be significant contributors to the development of LE injury. Conclusions: Decreased AP of the hip ER muscles was identified as a significant predictor for LE injury, whereas no hip abduction weakness or peak torque parameters were found to be predictive. Because controlling LE extremity movements is an important function of the hip muscles, they might be more challenged in a dynamic measure such as AP than in a point measure such as peak torque. Concentric AP of hip ER muscles can therefore be seen as an interesting factor to include in LE injury screening protocols.
Objective: To prospectively identify hip strength associated risk factors contributing to the development of lower extremity (LE) injury. Design: Data were prospectively collected on healthy female physical education students. Setting: This study was conducted in the institution of the University of Ghent. Participants: Eighty-nine female physical education students aged 19.53 ± 1.07 years. Assessment of Risk Factors: Testing included isokinetic hip strength measurements of abductors, adductors, internal rotators, and external rotators (ERs). Main Outcome Measures: Follow-up of the participants was assessed using a weekly online questionnaire and a 3-month retrospective control questionnaire. Lower extremity injury was diagnosed by an experienced medical doctor. Cox regression was used to identify the potential risk factors for the development of an LE injury. Results: Thirty-four participants were diagnosed with an LE injury during follow-up. This study identified that decreased average power (AP) (P = 0.031) on concentric ER strength was found to be a significant risk factor for LE injury. No other hip strength parameters were found to be significant contributors to the development of LE injury. Conclusions: Decreased AP of the hip ER muscles was identified as a significant predictor for LE injury, whereas no hip abduction weakness or peak torque parameters were found to be predictive. Because controlling LE extremity movements is an important function of the hip muscles, they might be more challenged in a dynamic measure such as AP than in a point measure such as peak torque. Concentric AP of hip ER muscles can therefore be seen as an interesting factor to include in LE injury screening protocols.https://ift.tt/2PxnS0K
Self-Reported Physical Activity Level in Student Athletes at Preparticipation Physical Evaluations
 Objective: Quantify physical activity in healthy student athletes. Design: Cross-sectional survey. Setting: Five Central Ohio schools during mass preparticipation physicals. Participants: Three hundred sixty-five children between the ages 10 and 18 years. Independent Variables: Days per week of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), minutes per day of MVPA, and number of activities. Main Outcome Measures: Minutes per week of MVPA. Results: One hundred eighty high school and 177 middle school subjects responded to the survey. There were 198 male and 162 female respondents. Mean age recorded 14.2 ± 1.7 years. There were no differences in activity volume based on sex. Mean minutes per week of MVPA reported 316.0 ± 231.0. High school subjects reported fewer activities than middle school cohort 2.7 ± 1.2 versus 3.2 ± 1.5 (P
Objective: Quantify physical activity in healthy student athletes. Design: Cross-sectional survey. Setting: Five Central Ohio schools during mass preparticipation physicals. Participants: Three hundred sixty-five children between the ages 10 and 18 years. Independent Variables: Days per week of moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), minutes per day of MVPA, and number of activities. Main Outcome Measures: Minutes per week of MVPA. Results: One hundred eighty high school and 177 middle school subjects responded to the survey. There were 198 male and 162 female respondents. Mean age recorded 14.2 ± 1.7 years. There were no differences in activity volume based on sex. Mean minutes per week of MVPA reported 316.0 ± 231.0. High school subjects reported fewer activities than middle school cohort 2.7 ± 1.2 versus 3.2 ± 1.5 (Phttps://ift.tt/2PxnG1w
AAP Updates Management of Sport-Related Concussion
FRIDAY, Nov. 14, 2018 -- Recommendations have been developed for the diagnosis and management of pediatric sport-related concussion (SRC), according to a clinical report published online Nov. 12 in Pediatrics. Mark E. Halstead, M.D., from the...
https://ift.tt/2QM4w4k
Epinephrine Personal Autoinjectors Cost-Effective at $24
FRIDAY, Nov. 16, 2018 -- In a simulation of children with peanut allergy, epinephrine personal autoinjectors are cost-effective at $24, according to a study published online Nov. 16 in JAMA Network Open. Marcus Shaker, M.D., from the...
https://ift.tt/2PCJ7yg
Effectiveness of golimumab in ulcerative colitis: A review of the real world evidence
Biologics against tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) have dramatically changed the management of moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis (UC). In pivotal clinical trials, golimumab showed efficacy as induction and maintenance therapy in anti-TNF naïve UC patients. However, confirmatory data on effectiveness in the real world setting are needed.
https://ift.tt/2QKsInL
Frequency and risk factors for liver disease following pancreatitis: A population-based cohort study
Both liver disease (LD) and pancreatitis pose substantial burdens. There have been no general population-based studies on frequency of LD after an episode of pancreatitis. The aim of this study was to investigate the occurrence of LD in a population-based cohort of patients following pancreatitis.
https://ift.tt/2Pziev0
Scientific American Article Highlights Focused Ultrasound for Alzheimer's
An article by Scientific American - "Battling Alzheimer's through Better Access to the Brain" - addresses recent clinical advances using focused ultrasound to disrupt the blood-brain barrier (BBB) to treat one of the most widespread neurodegenative disorders, Alzheimer's disease. According to the piece, "forty-four million people worldwide currently have Alzheimer's disease, and one in three people over 65 years of age will develop memory loss of some sort."
The article reports on a team at West Virginia University Rockefeller Neuroscience Institute that has launched a US clinical trial to investigate if opening the BBB in Alzheimer's patients can reduce the debilitating plaques and cognitive decline that are the hallmarks of the disease.
This work builds on a similar trial at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto that demonstrated the feasibility and preliminary safety of focally, reversibly, and repeatedly opening the BBB in six patients. The results of that trial were published in Nature Communications in July.
https://ift.tt/2PxEhlG
Symptom Trajectories Are Associated With Co-Occurring Symptoms During Chemotherapy For Breast Cancer
Symptoms are reported to co-occur during treatment for breast cancer. We previously identified 3 patterns of fatigue and 2 patterns of disturbed sleep, depressed mood, and anxiety in women undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer using a Latent Growth Mixture Model.
https://ift.tt/2A8NAy7
Edema of advanced cancer: prevalence, etiology and conservative management – a single hospice cross sectional study
Edema (accumulation of vascular pericapillary fluids) in patients at the end of life is a common distressing symptom seldom recognized in literature. The reported prevalence of edema reaches 11% of palliative care population.1 It may have multifactorial etiology – a combination of lymphatic congestion (lymphedema), increased capillary hydrostatic pressure (vascular edema), decreased plasma oncotic pressure (hypoproteinemic edema) and/or increased capillary permeability (permeability edema).2 In advanced cancer, recent retrospective chart review of 63 patients referred to palliative care edema service revealed that the most frequent issue was lower limb edema of mixed etiology, due to suspected blockage of lymphatics and/or patient's immobility.
https://ift.tt/2TlsSn6
-
This protocol presents an in vitro live-imaging phagocytosis assay to measure the phagocytic capacity of astrocytes. Purified rat astrocyt...
-
Association française pour l'étude du cancer [Imatinib in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in Morocco]. Related Articles [Im...
-
A Case of Miller Fisher Syndrome Due to the Use of Cemiplimab : No abstract available Miller Fisher syndrome is a rare, acquired n...


