|
Αρχειοθήκη ιστολογίου
-
►
2023
(138)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (74)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (64)
-
►
2022
(849)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (61)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (74)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (65)
-
▼
2021
(2936)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (59)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (180)
-
▼
Απριλίου
(241)
-
▼
Απρ 15
(17)
- Tumor immune landscape of paediatric high-grade gl...
- The role of gut dysbiosis in Parkinson's disease: ...
- COVID-19 neuropathology
- A neurogenetic analysis of female autism
- Monitoring skin blood flow to rapidly identify alt...
- Outcome of acute kidney injury: how to make a diff...
- Complex endovascular repair of type B aortic disse...
- Development and validation of a novel nomogram for...
- Article intro - Non-Technical Skill Assessment and...
- Neonatal Mast Cells and Transplacental IgE Transfe...
- Cancers, Vol. 13, Pages 1920: The Role of Rituxima...
- Review of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- Update on Endoscopic Therapies for the Treatment o...
- Alternative Surgical Anti-Reflux Procedures
- Increase of blood-brain barrier leakage is related...
- The initial CT blend sign is not associated with p...
- Acute motor and sensory axonal neuropathy in assoc...
-
▼
Απρ 15
(17)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (325)
-
►
2020
(1624)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (293)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (234)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (28)
-
►
2019
(13362)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (19)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (54)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (5586)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5696)
-
►
2018
(66471)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (5242)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (5478)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (4835)
- ► Ιανουαρίου (5592)
-
►
2017
(44259)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (5110)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (5105)
-
►
2016
(7467)
- ► Δεκεμβρίου (514)
- ► Σεπτεμβρίου (1038)
- ► Φεβρουαρίου (793)
Αναζήτηση αυτού του ιστολογίου
Πέμπτη 15 Απριλίου 2021
Tumor immune landscape of paediatric high-grade gliomas
The role of gut dysbiosis in Parkinson's disease: mechanistic insights andtherapeutic options
|
COVID-19 neuropathology
|
A neurogenetic analysis of female autism
|
Monitoring skin blood flow to rapidly identify alterations in tissue perfusion during fluid removal using continuous veno-venous hemofiltration in patients with circulatory shock
|
Outcome of acute kidney injury: how to make a difference?
|
Complex endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection and predicting left arm ischemia: a case report
|
Development and validation of a novel nomogram for individualized prediction of survival in cancer of unknown primary (CUP)
|
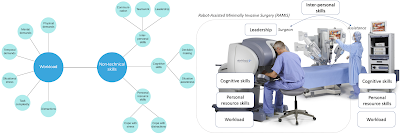
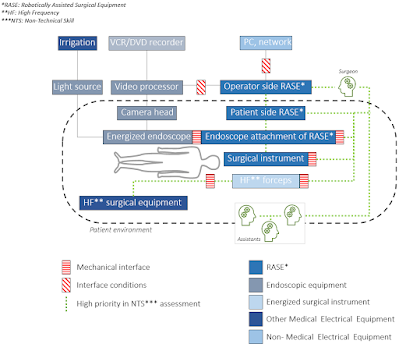
Article intro - Non-Technical Skill Assessment and Mental Load Evaluation in RAMIS
|
Neonatal Mast Cells and Transplacental IgE Transfer: A Mechanism of Disease Inheritance or of Passive Infant Barrier Defense?
|
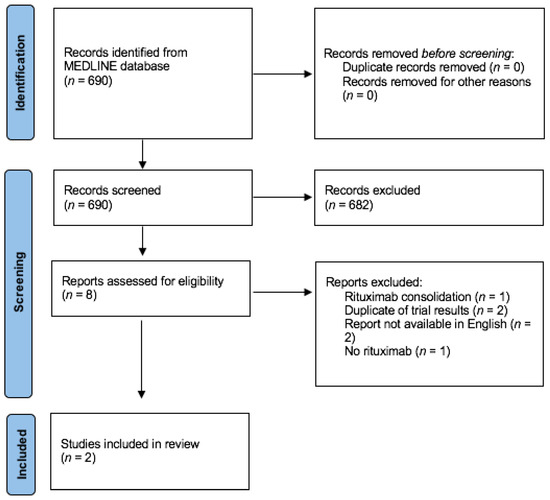
Cancers, Vol. 13, Pages 1920: The Role of Rituximab in the Treatment of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma
|
Review of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
|
-
This protocol presents an in vitro live-imaging phagocytosis assay to measure the phagocytic capacity of astrocytes. Purified rat astrocyt...
-
Measuring alterations in metabolic rates is central to understanding the progression of various diseases and aging. Here, we present a nov...
-
Association française pour l'étude du cancer [Imatinib in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in Morocco]. Related Articles [Im...