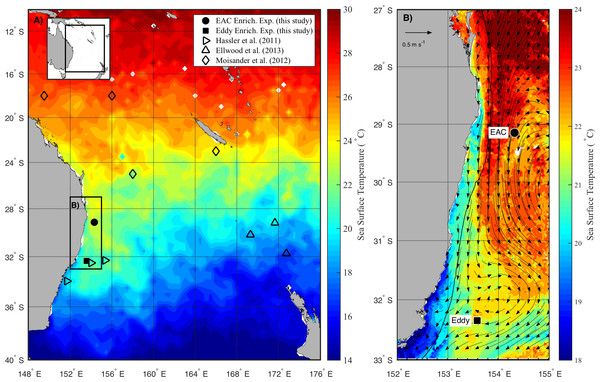
The intensification of western boundary currents in the global ocean will potentially influence meso-scale eddy generation, and redistribute microbes and their associated ecological and biogeochemical functions. To understand eddy-induced changes in microbial community composition as well as how they control growth, we targeted the East Australian Current (EAC) region to sample microbes in a cyclonic (cold-core) eddy (CCE) and the adjacent EAC. Phototrophic and diazotrophic microbes were more diverse (2–10 times greater Shannon index) in the CCE relative to the EAC, and the cell size distribution in the CCE was dominated (67%) by larger micro-plankton $(\geq 20\lrm{\mu }\mathrm{m})$ ≥ 20 μ m , as opposed to pico- and nano-sized cells in the EAC. Nutrient addition experiments determined that nitrogen was the principal nutrient limiting growth in the EAC, while iron was a secondary limiting nutrient in the CCE. Among the diazotrophic community, heterotrophic NifH gene sequences dominated in the EAC and were attributable to members of the gamma-, beta-, and delta-proteobacteria, while the CCE contained both phototrophic and heterotrophic diazotrophs, including Trichodesmium, UCYN-A and gamma-proteobacteria. Daily sampling of incubation bottles following nutrient amendment captured a cascade of effects at the cellular, population and community level, indicating taxon-specific differences in the speed of response of microbes to nutrient supply. Nitrogen addition to the CCE community increased picoeukaryote chlorophyll a quotas within 24 h, suggesting that nutrient uplift by eddies causes a 'greening' effect as well as an increase in phytoplankton biomass. After three days in both the EAC and CCE, diatoms increased in abundance with macronutrient (N, P, Si) and iron amendment, whereas haptophytes and phototrophic dinoflagellates declined. Our results indicate that cyclonic eddies increase delivery of nitrogen to the upper ocean to potentially mitigate the negative consequences of increased stratification due to ocean warming, but also increase the biological demand for iron that is necessary to sustain the growth of large-celled phototrophs and potentially support the diversity of diazotrophs over longer time-scales.
from #Medicine via ola Kala on Inoreader http://ift.tt/1SZ4sHj
via
IFTTT
Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου
Σημείωση: Μόνο ένα μέλος αυτού του ιστολογίου μπορεί να αναρτήσει σχόλιο.